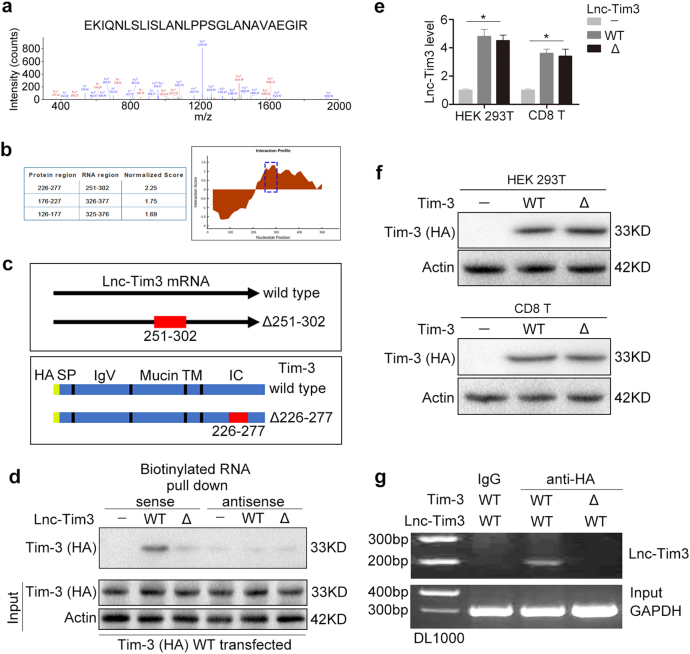
Fig. 2. Cytoplasmic Lnc-Tim3 specifically binds to Tim-3.
a Lnc-Tim3 RNA pull-down assay was performed. The associated proteins were processed and subjected to mass spectrometry followed by analysis via the Proteome Discoverer program. b The interaction between Tim-3 and Lnc-Tim3 was predicted by catRAPID method. c A schematic map of potential Tim-3 binding regions (wild type and Δ251-302) in the intracellular domain of Lnc-Tim3 (wild type and Δ226-277). d HEK 293 T cells were transfected with wild type Tim-3-HA (wild type) plasmid followed by lysis. Biotin-labeled sense and antisense of Lnc-Tim3 (wild type and Δ226-277) were used as probe. RNA pull-down assay was performed and the associated proteins were detected with anti-HA antibody. Representative of three experiments. e HEK 293 T and CD8 T cells were transfected with indicated lentiviral particles (vector, wild type or Δ226-277 Lnc-Tim3). The mRNA levels of Lnc-Tim3 were assessed by real-time PCR at 24 h after transfection. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M. n = 3, *P < 0.05. f HEK 293 T and CD8 T cells were transfected with indicated lentiviral particles (vector, wild type or Δ251-302 Tim-3-HA). The expression of Tim-3 (HA-tag) was assessed by western blot at 24 h after transfection. Representative of three experiments. g RIP assays were performed using HEK 293 T cells transfected with Tim-3-HA (wild type or Δ251-302) and Lnc-Tim3 (wild type), anti-HA antibody. The precipitated RNAs were determined by PCR for Lnc-Tim3 and GAPDH. Representative of three experiments