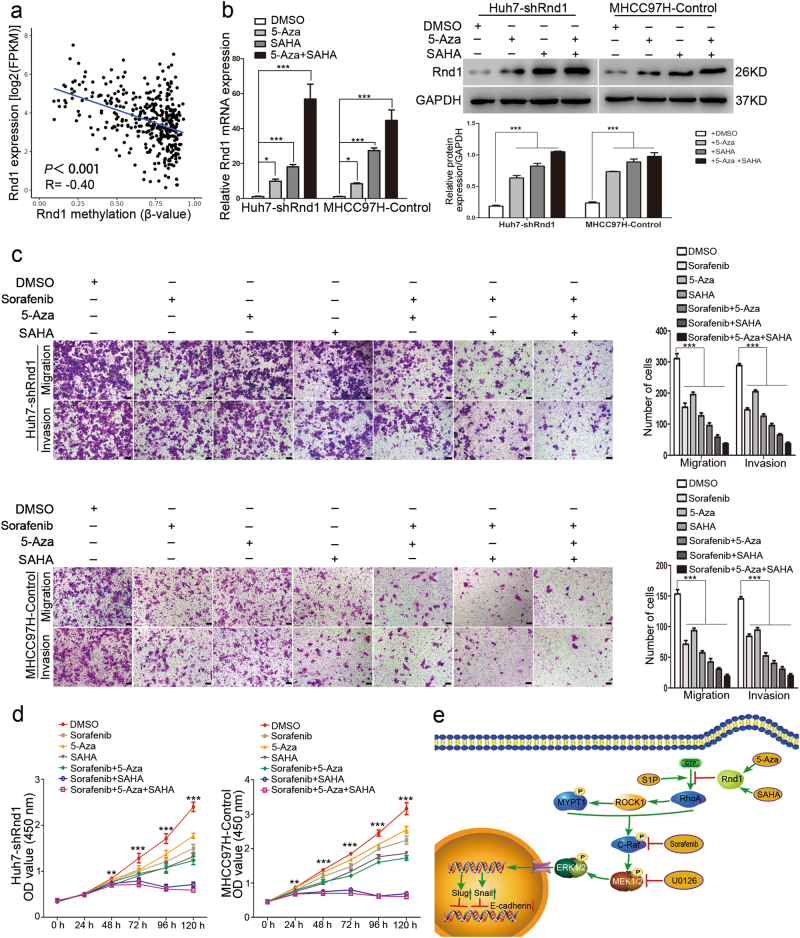
Fig. 7. The contribution of epigenetic mechanisms to Rnd1 silencing in HCC.
a The plot showed the relationship between Rnd1 expression and promoter methylation in TCGA data set. n = 396. b Detection of Rnd1 by Real-time PCR and Western blot in Huh7-shRnd1 and MHCC97H-Control cells after incubated with either 5-Aza (10 µM), SAHA (5 µM), or both compounds for 24 h. All data represent mean ± S.D. (n = 3) for three independent experiments. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA. *P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. c The cell migration and invasion evaluated by transwell assays with or without Matrigel in Huh7-shRnd1 and MHCC97H-Control cells treated with DMSO, sorafenib, 5-Aza, SAHA, sorafenib+5-Aza, sorafenib+SAHA or their mixture. Scale bar: 100 μm. Panel: quantification of migration and invasion of cells. Data are mean ± S.D. (n = 3) and are representative of three independent experiments. Significance was determined using one-way ANOVA. ***P < 0.001. d Changes in the growth rate of Huh7-shRnd1 and MHCC97H-Control cells treated with DMSO, sorafenib, 5-Aza, SAHA, sorafenib+5-Aza, sorafenib+SAHA or their mixture. Data are mean ± S.D. (n = 4) and are representative of three independent experiments. Significance was determined using two-way ANOVA. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. e Schematic of Rnd1 suppressing the Raf/MEK/ERK cascade by inhibiting the activation of RhoA and restraining EMT in HCC, and Rnd1 silencing could be overcome by 5-Aza and SAHA