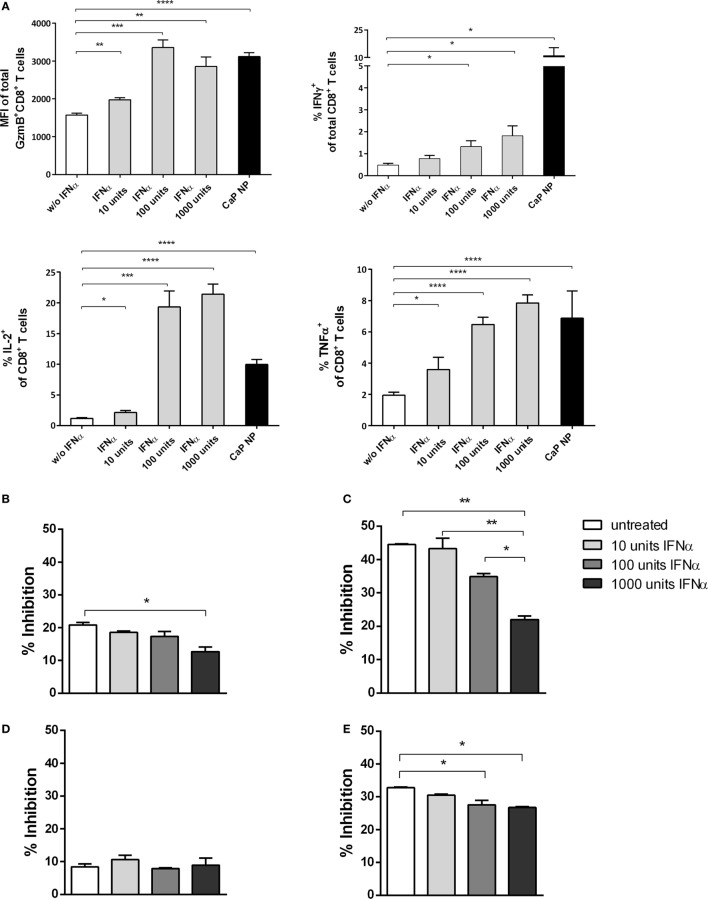
Figure 6.
CD8+ T cell and regulatory T cells (Treg) functionality is influenced by type I interferon (IFN I). (A) GagL peptide pulsed bone-marrow derived dendritic cells were co-cultured with FV-specific CD8+ T cells and stimulated with different amounts of universal IFN I. Expression of granzyme B, IFNγ, interleukin-2, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) was analyzed by intracellular cytokine staining. (B) Determination of the influence of IFN I on the suppressive capability of Tregs. Sorted CD4+ Foxp3+ (eGFP+) Treg cells from the spleen of naïve (B) or chronically FV infected (C) mice were co-cultured with CD8+ responder T cells and irradiated antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in the presence of αCD3 and different amounts of universal IFNα. (D) CD4+ CD25hi Treg cells were sorted from naïve IFNAR−/− mice and co-cultured with wild-type CD8+ responder T cells and irradiated IFNAR−/− APCs in the presence of αCD3 and different amounts of universal IFNα. (E) CD4+ Foxp3+ (eGFP+) Treg cells from naïve mice were co-cultured with CD8+ responder T cells and irradiated APCs both isolated from IFNAR−/− mice in the presence of αCD3 and different amounts of universal IFNα. Proliferation of CD8+ T cells was measured by the loss of eFluor dye, and inhibition was calculated. The results of two independent experiments are shown. Bars represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed by Student’s t-test (A) or ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (B–E) (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).