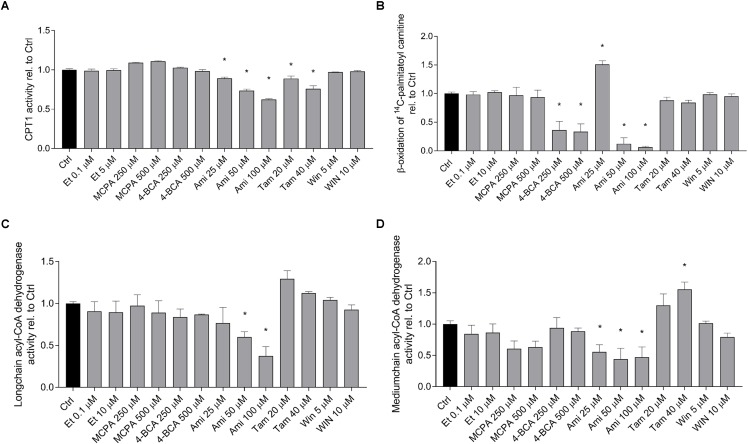
FIGURE 5.
Effect on fatty acid metabolism in isolated mouse liver mitochondria. Isolated, previously frozen mouse liver mitochondria were used as enzyme source. (A) Effect on CPT1A activity. Formation of 14C-palmitoylcarnitine from 14C-palmitoyl-CoA was assessed after incubation with the toxicants for 10 min. Basal rates of palmitoyl-CoA formation for control incubations (0.1% DMSO) were 3.0 ± 0.25 nmol palmitoyl-CoA × min-1 × mg protein-1. (B) Effect on 1-14C-palmitoylcarnitine metabolism. Mitochondria were treated with the toxicants for 10 min before formation of acid soluble products was determined. Basal rates of palmitoylcarnitine oxidation for control incubations (0.1% DMSO) were 213 ± 22 nmol palmitoylcarnitine × min-1 × mg protein-1. (C,D) Effect on long-chain and medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases. After pretreatment with the toxicants for 3 min, reduction of cytochrome c by FADH produced by the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases was determined spectrophotometrically. Basal rates of cytochrome c oxidation by long- and medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenases in control incubations (0.1% DMSO) were 53.7 ± 2.2 nmol × min-1 × mg protein-1 and 32.3 ± 1.2 nmol × min-1 × mg protein-1, respectively. Results were normalized to the values obtained in DMSO 0.1% exposed controls and are expressed as mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05 vs. DMSO 0.1% control.