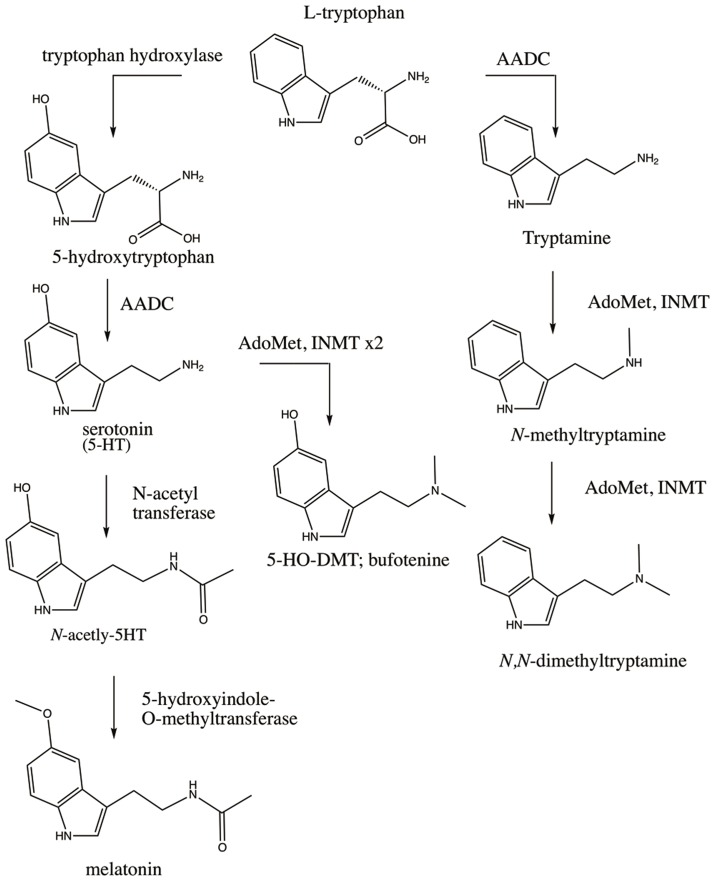
Figure 1.
Enzymatic pathways involved in the synthesis of the endogenous DMTs. Dietary tryptophan is the precursor for synthesis of serotonin (5-HT), melatonin, DMT, and 5-HO-DMT (bufotenine). DMT is synthesized via decarboxylation of tryptophan by AADC to produce tryptamine which is then double-methylated utilizing AdoMet as a methyl donor (rightmost pathway). Tryptophan can also be converted to 5-HT via hydroxylation by tryptophan hydroxylase and decarboxylation by AADC (leftmost pathway). 5-HT can be converted to melatonin via addition of an acetyl group by N-acetyl transferase and methylation by 5-hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase, or can alternatively be converted to bufotenine via methylation by INMT. Polymorphisms in these enzymes, the receptors their products bind to (e.g., 5-HT2A), and/or the metabolic enzymes that degrade their products (e.g., MAO) could affect the levels and effects of the endogenous DMTs through multiple permutations of SNPs as discussed throughout the manuscript.