Figure 8. M‐current contributes to persistent cholinergic excitation of CPn neurons.
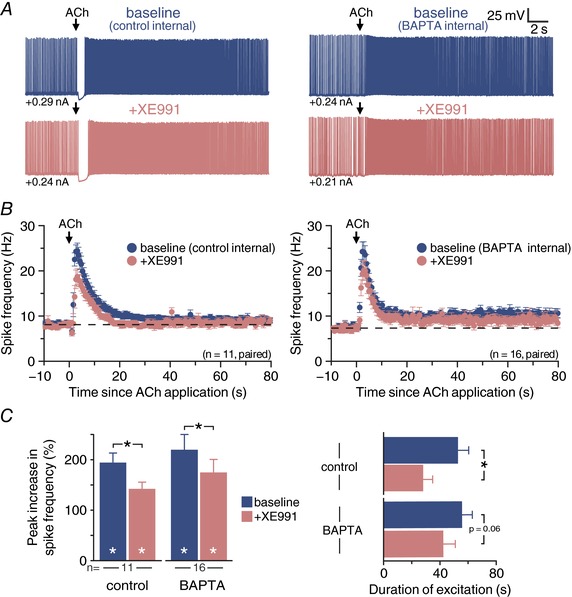
A, voltage responses to focal application of exogenous ACh (100 ms) in a CPn neuron recorded with control internal (left) or 10 mm BAPTA internal solution (right) in baseline conditions (top, blue) and after addition of the KV7 blocker XE911 (10 μm; bottom, pink). B, plot of mean ISFs for a population of CPn neurons (control internal, n = 11, left; 10 mm BAPTA internal, n = 16, right) in baseline conditions (blue) and after blockade of KV7 channels with XE991 (pink). C, comparisons of the magnitude (left) and duration (right) of cholinergic responses in baseline conditions and after addition of XE991 in control and BAPTA‐filled CPn neurons. Asterisks indicate significant differences (P < 0.05): white asterisks indicate significant changes from pre‐ACh firing frequencies, and black asterisks indicate significant differences between conditions.
