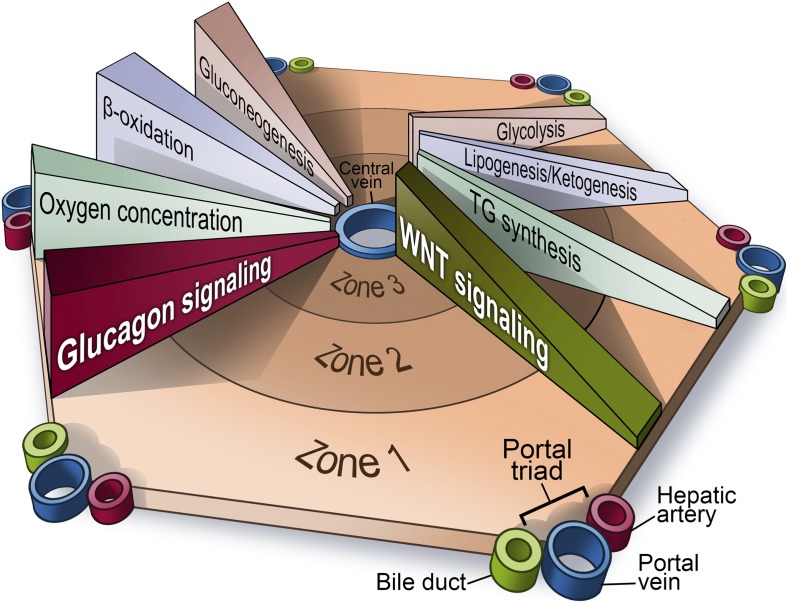
Fig. 1.
“Zonation” of different biochemical pathways in the liver. Zone 1 is defined as the region closest to the “portal triad,” consisting of the portal vein, the hepatic artery, and the bile duct. The innermost zone is located near the central vein, and is referred to as the pericentral region. Different anabolic and catabolic pathways are differentially active in different zones. A key “zonation modulator,” the Wnt/β-catenin pathway is active in the pericentral region near the central vein. The glucagon pathway, in contrast, displays its highest activity near the periportal region. TG, triglycerides. Image created by Richard Howdy (Visually Medical).