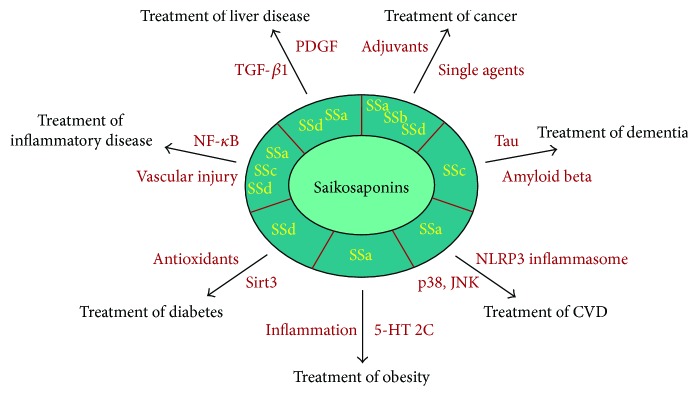
Figure 1.
The use of saikosaponins and implications for age-related diseases. Several types of saikosaponins, such as saikosaponin a (SSa), saikosaponin b (SSb), saikosaponin c (SSc), and saikosaponin d (SSd), could be used to treat age-related diseases. SSa, SSb, and SSd may be used for the treatment of cancer as single anticancer or adjuvant agents. Inhibitory actions of saikosaponins against P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance are implicated in the ability of saikosaponins to sensitize cancer cells to chemotherapy or radiotherapy. SSc has dual effects on human Alzheimer's disease by targeting both tau and amyloid beta. SSa may slow or reverse the progression of atherosclerosis by inhibiting oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced activation of p38 and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and assembly of the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 inflammasome. SSa exerts antiobesity activity by acting as a 5-hydroxytryptamine 2C receptor agonist or by suppressing extracellular signal-regulated kinase/nuclear factor- (NF-) κB pathway-induced inflammation. SSd provides protection against diabetic nephropathy through the upregulation of Sirt3 followed by mitochondrial antioxidant enzymes like isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 and manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase. SSa, SSc, and SSd may be used for the treatment of inflammatory disorders, such as asthma, arthritis, and sepsis, by downregulating the NF-κB signaling pathway or inhibiting vascular injury/apoptosis. Lastly, SSa and SSd protect the liver against age-associated injury and fibrosis by suppressing cytokines, including platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-β1.