Fig. 5.
Validation of DP1 as a true antigenic target in NT1 disease.
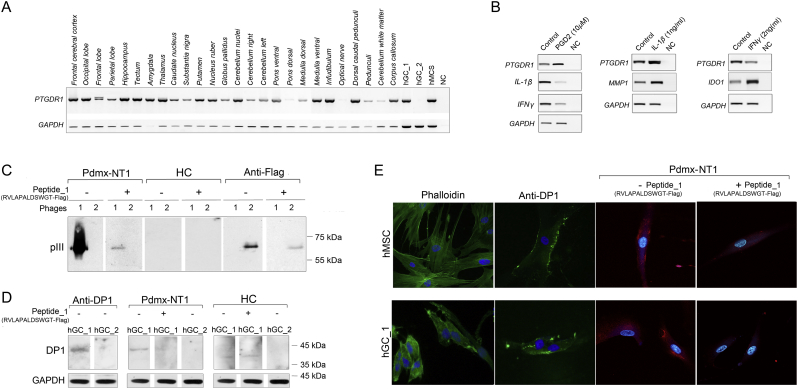
A. Human DP1 is expressed widely in different brain regions, and by mesenchymal and cancer stem cells. Cerebral cortex: Frontal cerebral cortex, Occipital lobe, Frontal lobe, Parietal lobe, Hippocampus; brain nuclei: Tectum, Amygdala, Thalamus, Caudate nucleus, Substantia nigra, Putamen, Nucleus ruber, Globus pallidus; Cerebellum: Cerebellar nuclei, Cerebellum right, Cerebellum left; Brainstem: Ventral pons, Dorsal pons, Dorsal medulla, Ventral medulla; Axonal tracts: Infundibulum, Optical nerve, Dorsal caudal pedunculi, Pedunculi, Cerebellum white matter, Corpus callosum; human glioma cells (hGC_1, hGC_2); human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC); NC – negative control. PCR analyses were done using specific primers for human DP1. GAPDH mRNA expression was used to normalize the data across samples.
B. PGD2/DP1 signaling is associated with inflammation regulation. Expressions of human DP1, IL-1β, MMP1, IFNγ and IDO-1 were analyzed by PCR in human mesenhymal stem cells treated with PGD2 (10 μM) or cytokines IL-1β (1 ng/mL) and IFNγ (2 ng/mL). NC – negative control. GAPDH mRNA expression was used to normalize the data across samples.
C. RVLAPALD was identified as a target antigen sequence for NT1-specific polyclonal IgG response. Western blot analysis of phage particles containing the RVLAPALD-pIII (phage 1) or FLAG-pIII fusion proteins (phage 2) show that human Pdmx-NT1 serum (dilution 1:500) reacted specifically with the pIII protein containing the peptide RVLAPALDSWGT sequence, but not with the phage backbone or FLAG-pIII fusion protein. Duplicate membranes were incubated with Pdmx-NT1 sera treated with the synthetic peptide (RVLAPALDSWGTGGGDYKDDD: final conc 6.6 μg/mL) that significantly blocked the interaction between phage #1 and human IgG similarly to anti-FLAG antibody (dilution 1:2000) and phage #2. RVLAPALDSWGT-pIII fusion protein was not detected by HC sera (1: 500). Protein size markers are indicated at the right side of blot.
D. NT1-specific seroreactivity to DP1 protein is specifically blocked by RVLAPALD peptide. Western blot analysis of endogenous levels of DP1 protein (MW 40 kDa) in human glioma hGC_1 and hGC_2 cells using anti-PTGDR1 (DP1) polyclonal antibodies (1:500) (left, first panels). Note that, hGC_2 cells were negative of DP1 expression. The use of the Pdmx-NT1 serum (1:500) showed similar pattern of DP1 reactivity in hGC_1 and hGC_2 cells, and the DP1-specific signal was attenuated by pre-treatments of Pdmx-NT1 sera with a synthetic peptide #1 (final conc 6.6 μg/mL). Anti-GAPDH monoclonal antibody (1:10,000) was used as a control for immunoblots.
E. DP1 expressed by hMSCs and cancer was specifically blocked by RVLAPALD peptide. IF analysis of DP1 in hMSC and glioma cells. The antibodies used included: anti-PTGDR1 (1:500; green), Pdmx-NT1 serum (1:400; red) and the secondary Alexa Flour 488 and 647 (Invitrogen, 1:2000) antibodies. For antibody-blocking, Pdmx-NT1 sera (1:400) and synthetic peptide #1 (final conc 6.6 μg/mL) were used. Cells were analyzed for phalloidin-labelled cytoskeleton proteins (green, left) and nuclear structures (Hoechst 33342, blue). Abbreviations: Pdmx-NT1- Pandermix-induced narcolepsy type 1; HC – healthy control.