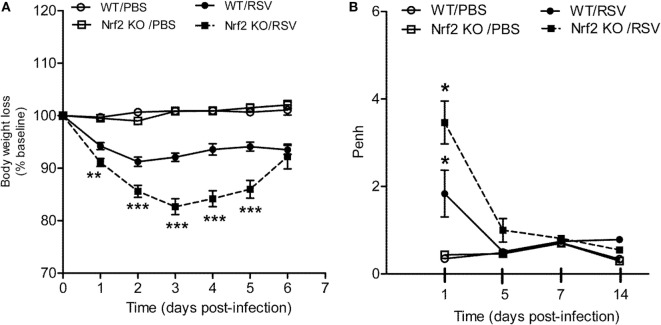
Figure 1.
NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) gene deficiency in mice exacerbates clinical disease and airway obstruction following respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. Under light anesthesia, groups of Nrf2 −/− (KO) and Nrf2 +/+ [wild-type (WT) control] mice were infected intranasally (i.n.) with 107 plaque-forming units (PFU) of RSV or PBS. (A) Mice were monitored daily for changes in body weight and disease manifestation. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 4–12 mice/group). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared with WT/RSV at days 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 post-infection. (B) Airway obstruction represented by baseline Penh was assessed by unrestrained plethysmography (Buxco Electronics, Inc., Sharon, CT). RSV-infected Nrf2 KO mice have increased airway obstruction compared to RSV-infected WT mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–8 mice/group). *p < 0.05 WT/RSV compared with WT/PBS, Nrf2 KO/RSV compared with Nrf2 KO/PBS, and Nrf2 KO/RSV compared with WT/RSV at day 1 post-infection.