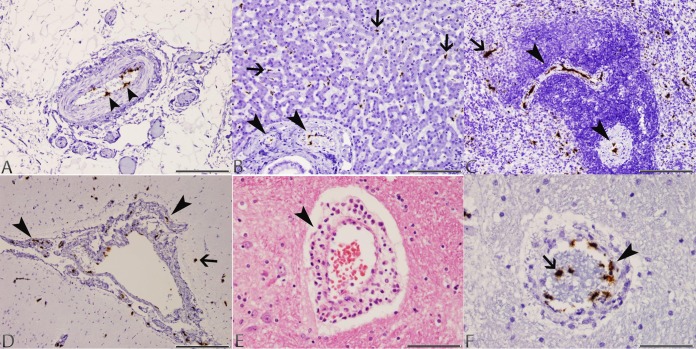
FIG 2.
Photomicrographs of tissues taken from dog 4 with typical lesions of CaVV infection. (A) Mesentery: CaVV nucleic acid signal in endothelial cells of a medium-sized arterial blood vessel (arrowheads) in the mesenteric attachment of the ileum (ISH; scale bar, 170 μm). (B) Liver: CaVV nucleic acid signal in endothelial cells of portal arterial blood vessels (arrowheads) and Kupffer cells along sinusoids (arrows) (ISH; scale bar, 170 μm). (C) Spleen: CaVV nucleic acid signal in endothelial cells of arterial blood vessels within the white pulp (arrowheads), and mononuclear cells within the red pulp (arrow; ISH; scale bar, 170 μm). (D) Brain: CaVV nucleic acid signal in endothelial cells of meningeal arterial blood vessels (arrowheads), and scattered glial cells in the cortex (arrow) (ISH; scale bar, 330 μm). (E) Brain: perivascular cuff of lymphocytes and macrophages within the cerebrum (arrow) (H&E; scale bar, 85 μm). (F) Brain: CaVV nucleic acid signal in endothelial cells (arrowhead) and circulating intravascular leukocytes (arrow) in a medium-sized arterial blood vessel (ISH; scale bar, 85 μm).