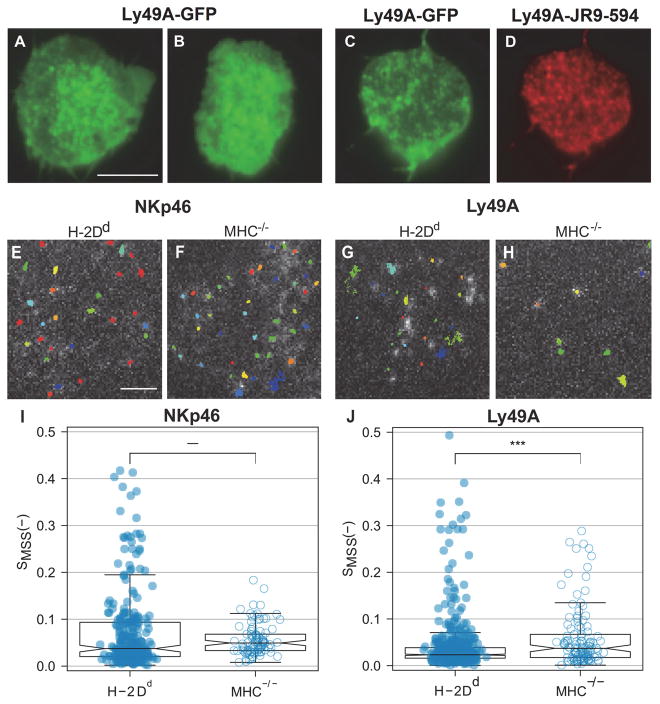
Fig. 1. Dynamic confinement of NKp46 and Ly49A at the NK cell surface.
(A–D) Representative fluorescence images showing transfected Ly49A-GFP in CHO cells. The images were merged from 6000 frames acquired at a 36 ms frame-to-frame rate. (A–B) Transfected Ly49A-GFP without antibody labeling (C) Transfected Ly49A-GFP incubated with an antibody that recognizes Ly49A (clone JR9.318 conjugated to abberior star 594). (D) The JR9.318-abberior star 594 labeling in the same cell as in panel C. (E–J) Single particle tracking (SPT) in freshly isolated H-2Dd compared to MHC−/− murine Ly49A+ NK cells captured at a 20 ms frame-to-frame rate. (E–H) Representative single particle tracks of NKp46 (E, F), and Ly49A (G, H) in H-2Dd and MHC−/− NK cells. (I, J) The degree of anomalous diffusion (Hurst parameter) for NKp46, median H-2Dd = 0.037 and MHC−/− = 0.049 (I), and Ly49A, median H-2Dd = 0.023 and MHC−/− = 0.037 (J), was calculated on 100 frames segments of trajectories. All the values calculated for a single trajectory were averaged. Each dot represents a single trajectory, H-2Dd NKp46 N=264, MHC−/− NKp46 = 94, H-2Dd Ly49A = 521, and MHC−/− Ly49A = 116. Data was pooled from 7 – 27 cells per group, from three to six independent experiments. The boxes represent medians (line inside box), the 95 % confidence intervals (notches), first and third quartiles (end of boxes), and the whiskers 1.5 times the interquartile ranges. P-values: *** ≤ 0.001 (two-sample Wilcoxon ranking test). Scale bars, 5 μm (A–D) and 2 μm (E–H).