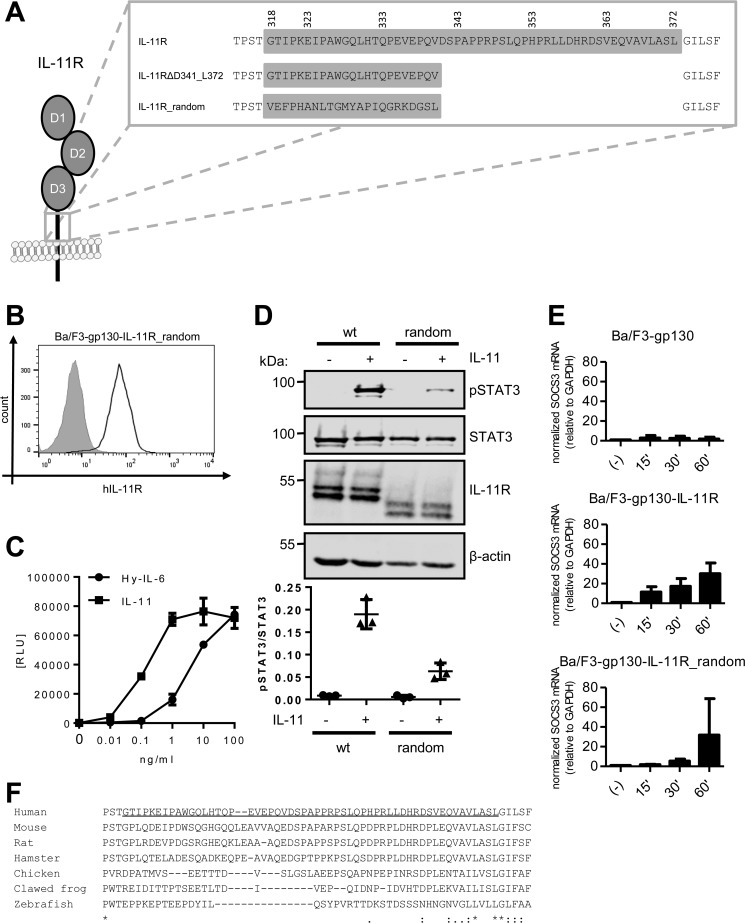
Figure 7.
Classic IL-11 signaling is independent of the stalk sequence. A, stalk sequences of IL-11R, IL-11RΔD341_L372, and IL-11R_random. B, cell surface expression of IL-11R_random was assessed by flow cytometry. C, equal amounts of Ba/F3–gp130–IL-11R_random cells were stimulated with increasing amounts (0–100 ng/ml) of either IL-11 or Hy–IL-6 for 48 h. Concentration-dependent proliferation was determined as described in “Experimental Procedures.” D, STAT3 phosphorylation of Ba/F3–gp130–IL-11R_random in response to 10 ng/ml IL-11 or 10 ng/ml Hy–IL-6 stimulation for 15 min was determined by Western blotting. Total STAT3 was determined to ensure equal protein loading. The ratio of pSTAT3/STAT3 was determined from three independent experiments. E, Ba/F3-gp130, Ba/F3–gp130–IL-11R and Ba/F3–gp130–IL-11R_random cells were stimulated with 10 ng/ml IL-11 for the indicated time points. The relative amounts of SOCS3 mRNA were quantified as described in the legend to Fig. 5B. Values were normalized to GAPDH (n = 3 independent experiments, three technical replicates per experiment, mean ± S.D.). F, sequence alignment of the amino acid residues of the IL-11R stalk sequences from human (Homo sapiens), mouse (Mus musculus), rat (Rattus norvegicus), hamster (Mesocricetus auratus), chicken (Gallus gallus), clawed frog (Xenopus tropicalis), and zebrafish (Danio rerio). The predicted stalk region of the human IL-11R has been underlined.