Figure 3.
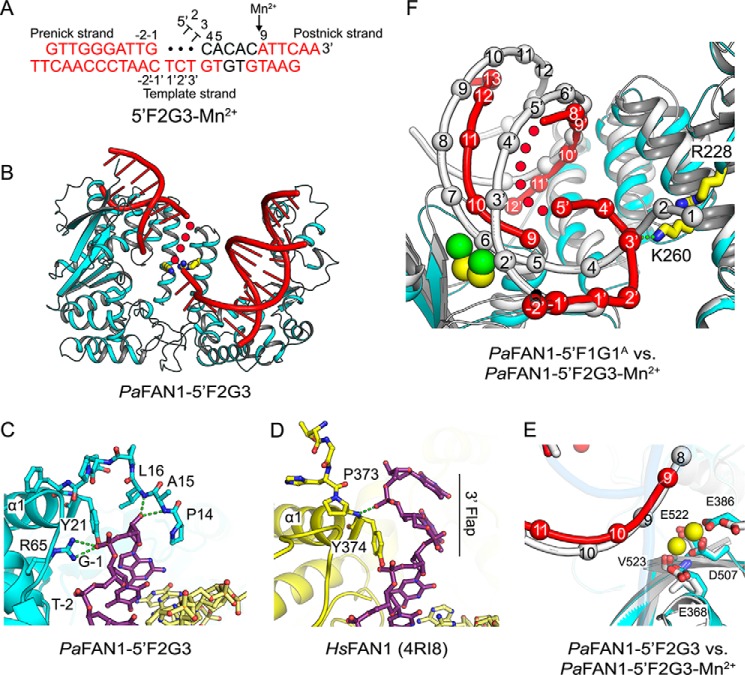
Crystal structure of PaFAN1–5′F2G3 in the presence or absence of Mn2+. A, scheme of 5′F2G3 DNA used for crystallization. Disordered bases are colored in black, and unpaired bases at a gap are shown as filled circles. Scissile phosphates are indicated by a black arrow. B, overall structure of the PaFAN1–5′F2G3. C, close-up view of the interaction between the N-terminal loop of PaFAN1 and the pre-nick duplex. D, N-terminal loop of HsFAN1 and the 3′ flap. See also Fig. S1. E, close-up view of the active site in the PaFAN1–5′F2G3 in the presence (colored as in Fig. 1B) or absence (protein and DNA in gray) of Mn2+ ions. F, superposition of the PaFAN1–5′F2G3-Mn2+ (protein, DNA, and Mn2+ ions are colored in cyan, red, and yellow, respectively) and PaFAN1–5′F1G1A (protein and DNA in gray; Ca2+ ions in green) structures. Structures are aligned through their NTD. The gap region is flipped and interacts with the Arg/Lys patch. See also Fig. S2.