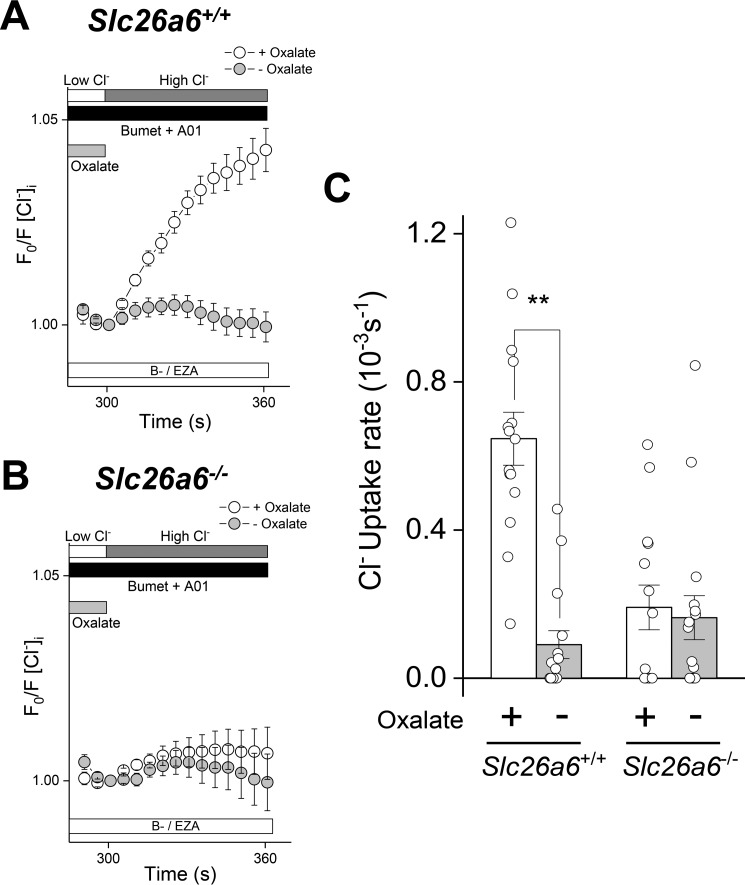
Figure 5.
Slc26a6 mediates Cl−/oxalate exchange in mouse SMG acinar cells. Acinar cells isolated from Slc26a6+/+ and Slc26a6−/− submandibular glands were loaded with SPQ to monitor Cl− uptake. Cl− depletion was induced by incubation in a low Cl− solution in the absence (− Oxalate) or presence (+ Oxalate) of 25 mm oxalate, and then Cl− uptake was stimulated by reintroduction of high extracellular Cl− in the absence of oxalate. Experiments were performed in bicarbonate-free solutions containing ethoxyzolamide (30 μm B−/EZA) to eliminate Cl−/HCO3− exchange and T16Ainh-01 (10 μm A01) and bumetanide (Bumet, 80 μm) to inhibit Tmem16a and Nkcc1, respectively. A, oxalate-dependent Cl− uptake was observed in Slc26a6+/+ SMG acinar cells, but no Cl− uptake was observed when oxalate was absent (+ Oxalate, open circles, n = 15; − Oxalate, closed circles, n = 15). B, Cl−/oxalate exchange activity was absent in SMG acinar cells from Slc26a6−/− mice (+ Oxalate, open circles, n = 14; − Oxalate, closed circles, n = 16). C, summary of the Cl− uptake experiments shown in A and B. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. of cells isolated from at least four different mice per group. Statistical analysis was performed using unpaired t test; **, p < 0.01.