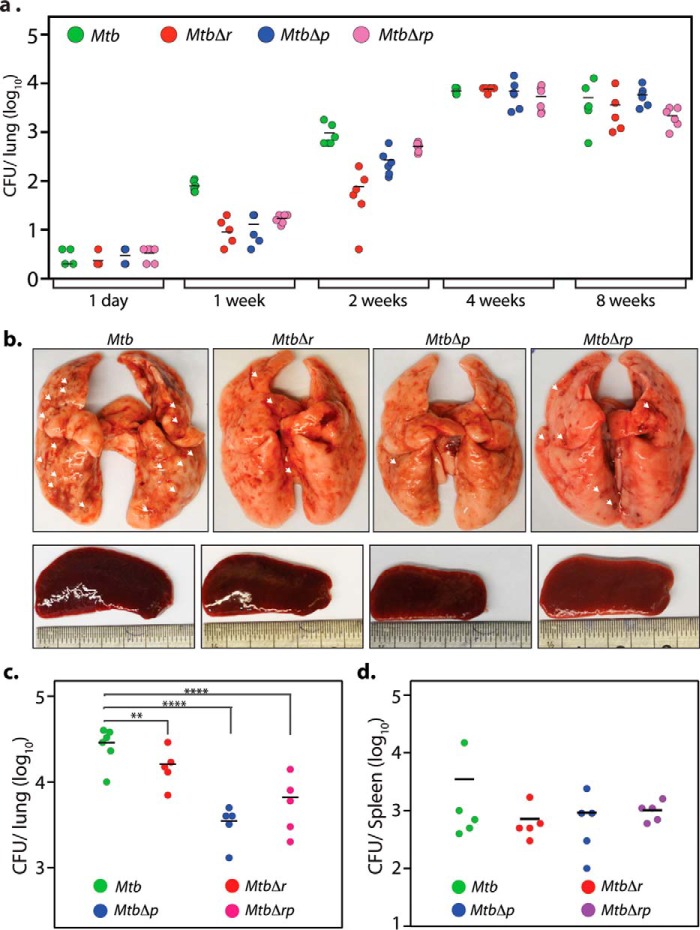
Figure 9.
RodA and PbpA are important for pathogen survival in the host. a, 5 mice/group/time point were aerosolically infected with 200 cfu/lung of Mtb, MtbΔr, MtbΔp, and MtbΔrp strains. cfu were enumerated in the lungs of infected mice after day 1 (4 mice/group), 1, 2, 4, and 8 weeks (5 mice/group) postinfection. b–d, 5 guinea pigs/group/time point were infected with Mtb, MtbΔr, MtbΔp, and MtbΔrp strains, and animals were sacrificed at 4 weeks postinfection. b, representative images for gross assessment of lungs and spleen from infected guinea pigs 4 weeks postinfection. Discrete tubercles in the lungs are shown with white arrows. c and d, cfu enumeration from the infected lungs (c) and spleen (d). Mean cfu values in the lungs of guinea pigs (c) infected with Mtb, MtbΔr, MtbΔp, and Mtbrp were 4.51, 4.2, 3.54, and 3.81 on the log10 scale, respectively. Statistical analysis was performed using a one-way ANOVA test. ****, p < 0.0001; **, p < 0.01. Mean cfu values in the spleens of guinea pigs (d) infected with Mtb, MtbΔr, MtbΔp, and Mtb were 3.44, 3.41, 3.39, and 3.54 on the log10 scale, respectively.