Figure 6.
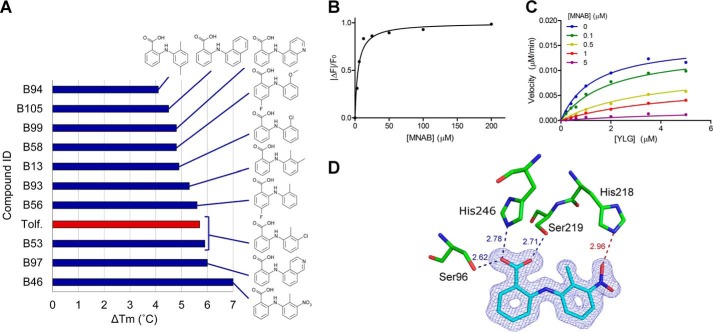
SAR study of DAD2 inhibitors. A, structures of the top 10 compounds of the SAR study, as assessed by decreasing values of DAD2's melting temperature shifts in the DSF assay. The red bar corresponds to known tolfenamic acid (Tolf.) used as reference. The experimental melting curves and derivatives of the melting curves for DAD2 in the presence of the top 10 compounds are shown in Fig. S5. Compound IDs for the SAR study were B1–B136, as detailed in Table S3. B, binding of MNAB to DAD2 using intrinsic fluorescence experiments. Each data point is the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of three technical replicates. C, competition of YLG hydrolysis by DAD2 using MNAB. Each data point is the average of three technical replicates. All of the individual replicates for each compound concentration were included during the nonlinear global fit analysis using a mixed-inhibition model. D, MNAB bound to DAD2. The final σA-weighted map contoured at 1.0σ around MNAB is shown in dark blue (the corresponding omit map is shown in Fig. S2). DAD2 residues involved in polar interactions with MNAB are shown. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines, with distances (in Å) between polar atoms indicated. The additional hydrogen bond between the nitro group of MNAB and His246 is shown as a dotted red line. See also Table S2.