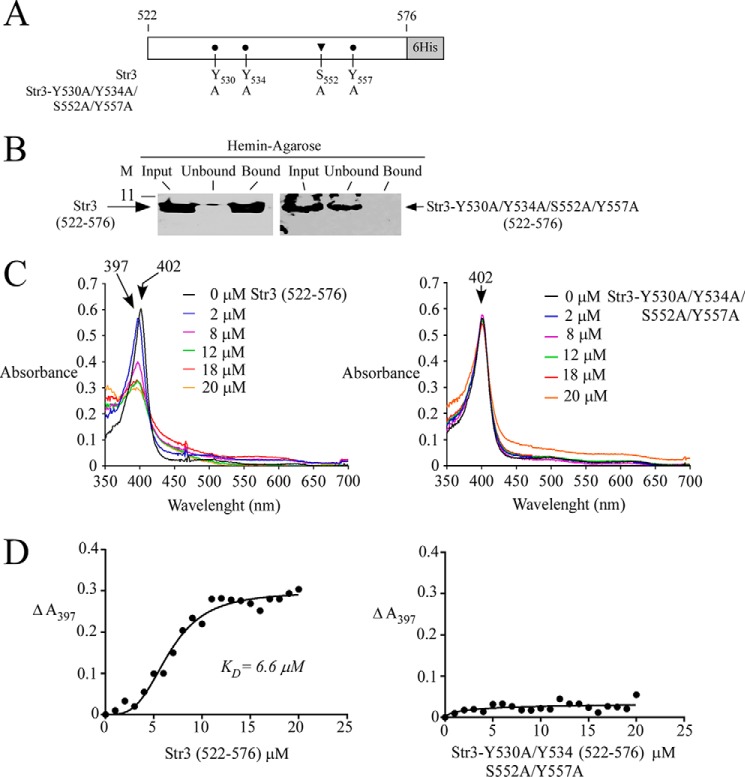
Figure 8.
Str3(522–576) and hemin interact with one another. A, schematic representation of the Str3(522–576) region and its mutant derivative. B, purified WT Str3(522–576) (left) or Str3-Y530A/Y534A/S552A/Y557A)(522–576) mutant (right) (Input) was incubated with hemin-agarose beads. Unbound and bound purified WT or mutant Str3(522–576) was analyzed by immunblot assays using an anti-His6 antibody. C, differential spectral titration of WT Str3(522–576)-hemin interaction (left) using 5 μm hemin and increasing concentrations of Str3 (0–20 μm). Similar titration assays (right) were performed with increasing concentrations of Str3-Y530A/Y534A/S552A/Y557A(522–576) mutant (0–20 μm) and hemin (5 μm). D, hemin-binding curves for WT (left) and mutant (right) Str3(522–576) obtained by plotting changes in absorbance at the Soret peak as a function of Str3 concentrations. WT Str3(522–576) and hemin interacted with one another with a KD of 6.6 × 10−6 m.