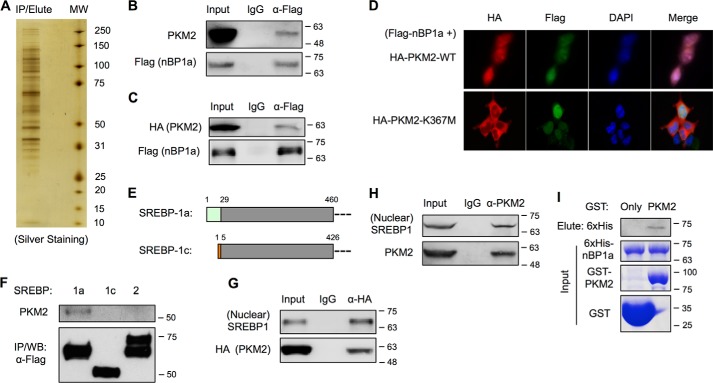
Figure 1.
SREBP-1a interacts with PKM2. A, silver staining of nBP1a-binding proteins that were immunoprecipitated from nuclear extracts of HEK293T cells stably transfected with FLAG–nBP1a. B, co-IP analysis of endogenous PKM2 binding to overexpressed FLAG–nBP1a in HepG2 cells. The presence of PKM2 in IP eluates was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-PKM2 antibody. C, co-IP analysis of overexpressed HA-PKM2 binding to overexpressed FLAG–nBP1a in HepG2 cells. D, immunostaining to analyze the localization of co-transfected HA-PKM2 and FLAG–nBP1a in HepG2 cells. E, diagram shows the sequence difference between SREBP-1a and SREBP-1c. F, co-IP analysis of endogenous PKM2 binding to overexpressed FLAG-tagged nuclear forms of SREBP-1a, SREBP-1c, and SREBP-2 in HEK293T cells. G, co-IP analysis of overexpressed HA-PKM2 binding to endogenous nuclear form of SREBP-1 in HepG2 cells. H, co-IP analysis of endogenous PKM2 binding to endogenous nuclear form of SREBP-1 in HepG2 cells. I, GST pulldown analysis of interaction between recombinant PKM2 and SREBP-1a. WB, Western blotting.