FIGURE 4.
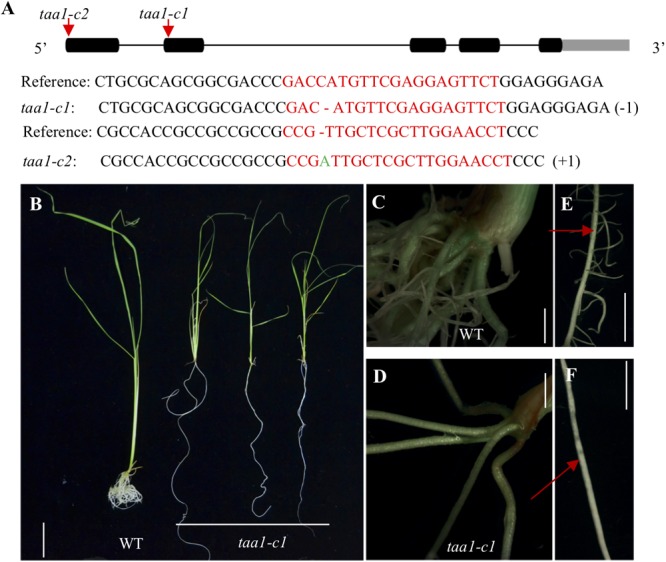
Generation of CRISPR mutations in the TAA1 gene in rice and characterization of the root defects of the taa1 mutants. (A) Two independent alleles of taa mutants (taa1-c1 and taa1-c2, c stands for CRISPR) were generated using CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing technology as described in the Materials and Methods. The mutations were located inside the TAA1/FIB1 target sequence. The arrows indicate CRISPR/Cas9 target sites, which were located inside the first and the second exon, respectively. The taa1-c1 had one 1 bp deletion and the taa1-c2 contained 1 bp insertion. (B) Comparison of the seedlings of taa1-c1 homozygous mutants with WT. The taa1-c1 mutant had longer seminal root and fewer crown roots compared to WT. Bar = 3 cm. (C–D) The detailed root images of WT and taa1-c1 homozygous mutants, respectively. The taa1-c1 mutant failed to develop crown roots. Bar = 0.2 cm. WT plants developed lateral roots (E) whereas taa1-c1 did not have lateral roots (F). Bar = 0.5 cm.
