Fig. 4.
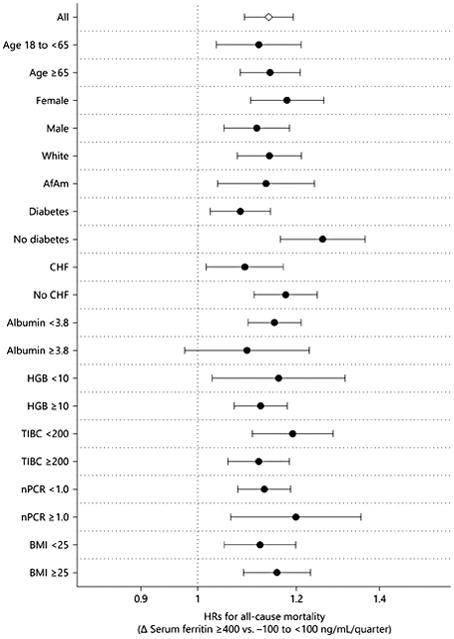
Case-mix and MICS-adjusted HRs (95% CIs) of all-cause mortality associated with increase of change in serum ferritin ≥400 ng/mL/quarter across subgroups of age (<65, ≥65 year-old), sex (female, male), race (white, African American), diabetes, CHF, serum albumin (<3.8, ≥3.8 g/dL), hemoglobin (<10, ≥10 g/dL), TIBC (<200, ≥200 mg/dL), nPCR (<1.0, ≥1.0 g/kg/day), and BMI (<25, ≥25 kg/m 2). AfAm, African American; BMI, body mass index; CHF, congestive heart failure; HGB, hemoglobin; nPCR, normalized protein catabolic rate; TIBC, total iron binding capacity.
