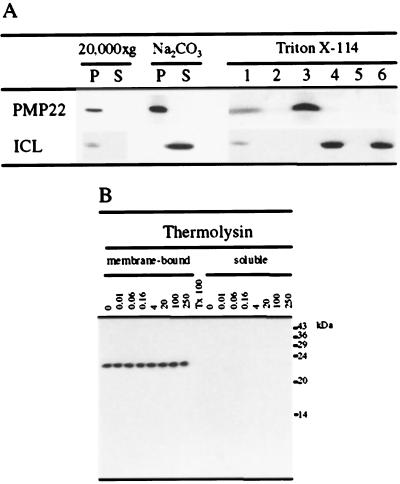
Figure 6.
A, PMP22 is resistant to extraction by Na2CO3 and partitions in the detergent phase of Triton X-114. A 20,000g organelle pellet (P) and the corresponding supernatant (S) were prepared from dark-grown tissue-cultured cells and analyzed for PMP22 and isocitrate lyase (ICL) by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting (20,000g). The 20,000g pellet fraction enriched in PMP22 was treated with 0.1 m Na2CO3 (pH 11.0) and centrifuged at 100,000g to produce a membrane pellet and supernatant fraction. A postnuclear supernatant prepared from dark-grown tissue-cultured cells was fractionated using 2% (v/v) Triton X-114 phase separation, and the various fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with antibodies against isocitrate lyase and affinity-purified anti-PMP22 antibodies. Lane 1, Postnuclear supernatant; lane 2, Triton X-114-insoluble pellet; lane 3, detergent phase; lane 4, aqueous phase; lane 5, “glycoprotein”-rich pellet; and lane 6, postaqueous supernatant. In all lanes 150 μg of protein was analyzed. B, Accessibility of Arabidopsis PMP22 to protease. The peroxisome-enriched 20,000g pellet fraction was subjected to hypotonic lysis followed by a wash with 250 mm NaCl. Salt-washed membranes (250 μg) were incubated with the protease thermolysin at the indicated concentrations (see Methods). After the incubation the protease was inhibited and the membrane-bound and protease-solubilized peptides were separated by ultracentrifugation. Triton X-100 was included in a duplicate incubation containing 100 μg mL−1 thermolysin, which was not subjected to ultracentrifugation before analysis by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting. All samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting with affinity-purified anti-PMP22 antibodies.