Figure 6.
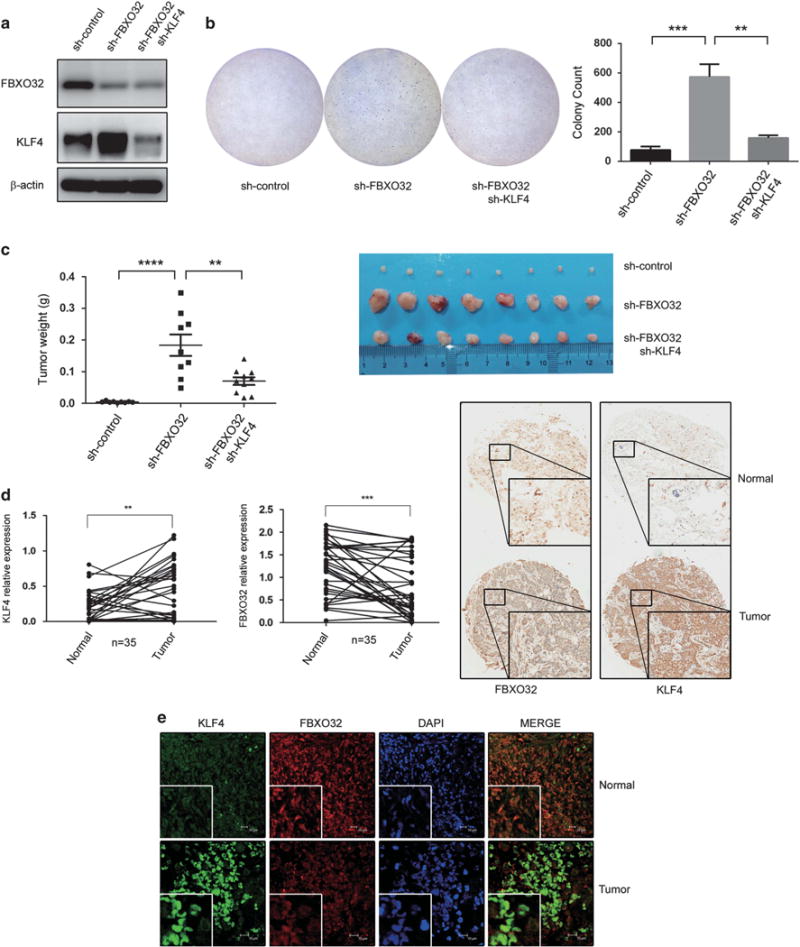
FBXO32 facilitates tumorigenesis both in vitro and in vivo. (a) FBXO32/KLF4 double knockdown MCFCA1a cells. MCFCA1a cells with FBXO32 stable knockdown and FBXO32/KLF4 double knockdown were developed using a lentivirus system. Expression of FBXO32 and KLF4 were analyzed by western blot. (b) FBXO32 inhibits tumorigenesis through mediating proteasomal degradation of KLF4 in MCFCA1a cells. In all, 30 000 MCFCA1a cells were plated in 60-mm dish to grow in soft agar. Three weeks later, the cells were dyed with crystal violet and the colony numbers were counted. (c) FBXO32 inhibits tumorigenesis through mediating proteasomal degradation of KLF4 in a mouse model. In total, 4 × 105 MCFCA1a cells were injected orthotopically into BALB/c nude mice (n = 8). The mice were killed 3 weeks later. The xenografts were weighed and image of primary tumors was presented. (d) Tissue microarray sections were stained by KLF4 and FBXO32 antibodies. Representative staining of KLF4 and FBXO32 (20 ×) was shown and the tissue staining was quantified and analyzed. (e) Immunofluorescent double staining of human breast cancer tissues. Tissue microarray section was immunoblotted by KLF4 and FBXO32 antibodies and labeled with second antibody conjugated with FITC and CY3. Immunofluorescence labeled tissue samples were then scanned by laser confocal microscopy. Representative staining were presented. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.
