Figure 1.
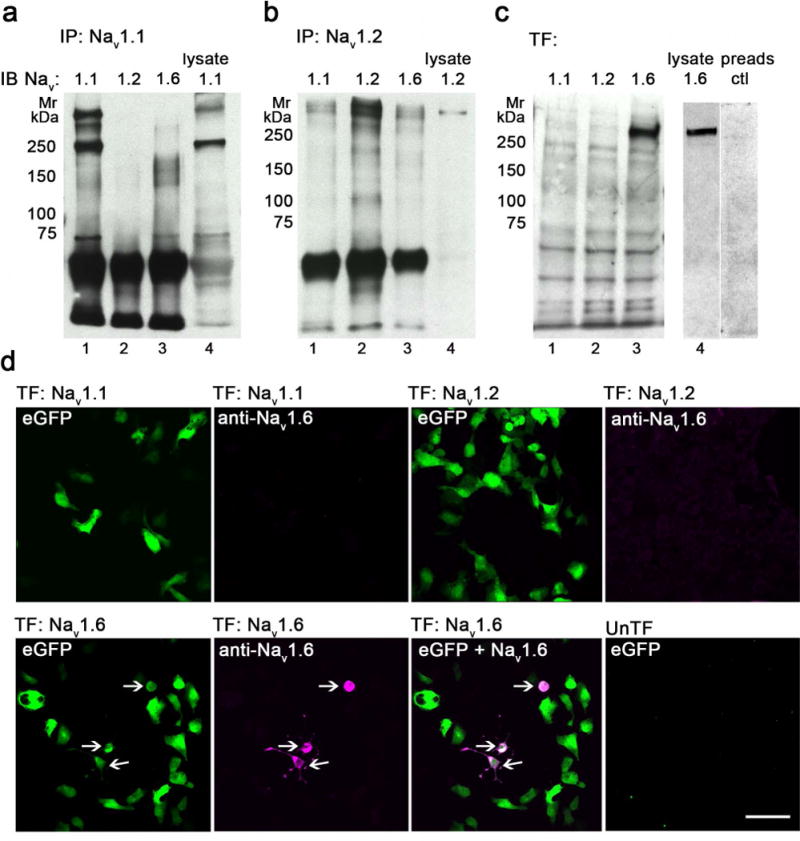
Validation of anti-Nav 1.1, anti-Nav 1.2 and anti-Nav 1.6 specificities. A-B. Nav 1.1 (A) and Nav 1.2 (B) were immunoprecipitated (IP) from rat brain hippocampus lysates and immunoblotted (IB) with anti-Nav 1.1, anti-Nav 1.2, and anti-Nav 1.6 antibodies (lanes 1-4). C. HEK293FT cells were transfected (TF) with human Nav 1.1 (lane 1), rat Nav 1.2 (lane 2) or mouse Nav 1.6 (lane 3) and immunoblotted with anti-Nav 1.6 antibody. Hippocampal lysate (lane 4) and a pre-adsorption peptide (lane 5) were used as a positive and negative control, respectively. The blocking peptide, made up of the same sequences as the Nav 1.6 antibody, specifically blocks expression of Nav 1.6 from the hippocampal lysate. D. HEK293FT cells were transfected (TF) with eGFP (green fluorescence) and human Nav 1.1 (top left 2 panels), rat Nav 1.2 (top, right 2 panels) or mouse Nav 1.6 (bottom 3 panels), and immunolabeled with anti-Nav 1.6 with detection using AlexaFluor-568-conjugated secondary antibody (magenta fluorescence). All cells expressing Nav 1.6 co-expressed eGFP (arrows). Untransfected cells (bottom right) served as a negative control. Mr, relative molecular mass (in kDa). Bar 75 μm. See supplemental figure 1 for red-green images.
