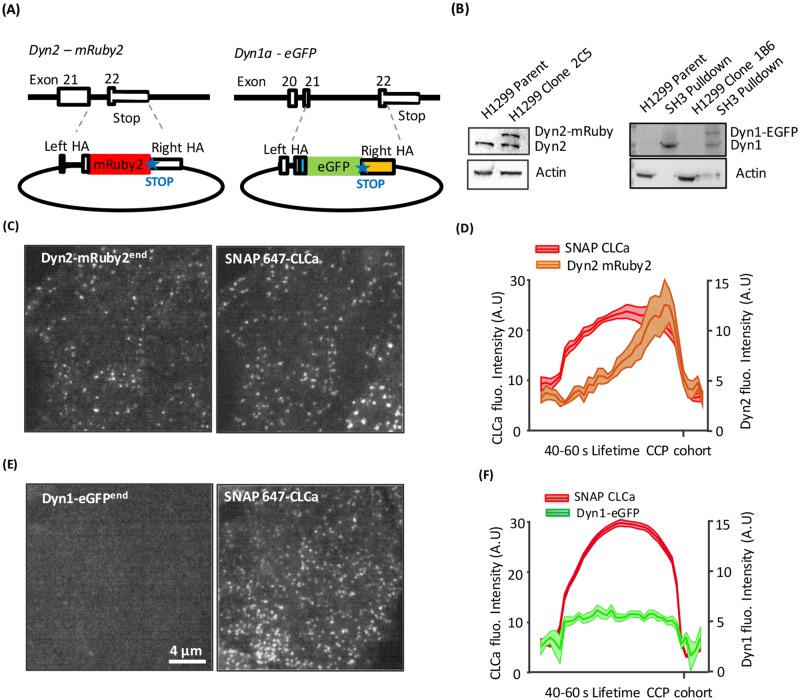
Fig 1. Isoform-specific differences in recruitment of dynamin to CCPs.
(A) Diagram of Zinc-finger and CRISPR/Cas9n knock-in strategies for endogenous labeling of Dyn2 and Dyn1 in H1299 cells with C-terminal mRuby2 and eGFP tags, respectively. For Dyn2, a short linker and mRuby2 (red) were placed at the stop codon in exon 22. For canonical Dyn1 splice isoform “a,” the 19 C-terminal amino acids (blue) were inserted in exon 21, followed by a short linker, eGFP (green), with stop codon and a polyadenylation sequence (yellow). In both constructs, flanking homology arms (HAs) of roughly 800 bp were used to promote recombination (dashed lines). See S1 Fig for details. (B) Western blot analysis of tagged isoforms. The low levels of Dyn1 in H1299 cells could not be directly detected by western blotting but can be detected after pulldown with GST-Amphiphysin II SH3 domains. Representative TIRF images (see S1 and S2 Movies) showing membrane recruitment of endogenous Dyn2-mRuby2end (C) or Dyn1a-eGFPend (E) and corresponding lentiviral transduced SNAP(647)-CLCa images. (D,F) Clathrin labeled puncta were identified and thresholded to define bona fide CCPs [22]. Shown are the averaged kinetics of recruitment of SNAP-CLCa and Dyn2-mRuby2end (D) or Dyn1a-eGFPend (F) for all tracks with lifetimes between 40 and 60 s (831 CCPs from 5 movies containing a total of 15 cells for Dyn2-mRuby2end and 13,346 CCPs from 10 movies containing a total of 29 cells for Dyn1a-eGFPend). CLCa, clathrin light chain a; CRISPR/Cas9n, Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats-associated nucleases 9 nickase; Dyn1, dynamin-1; GST, Glutathione S-transferase; HA, homology arm; SH3, SRC Homology 3.