Figure 1.
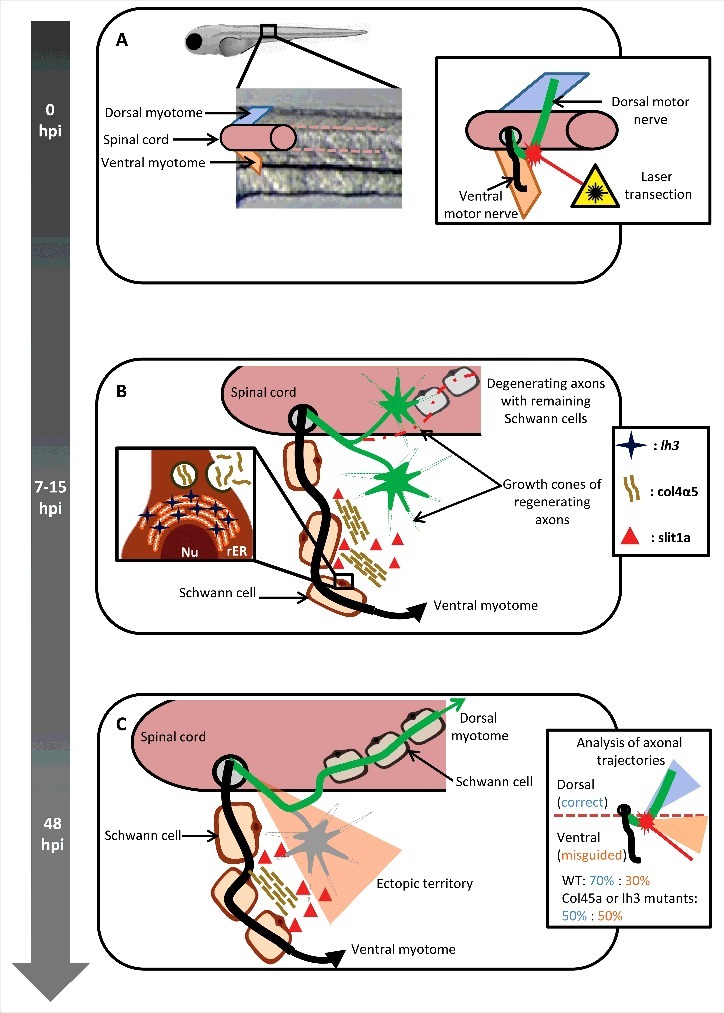
Peripheral glia regulates axonal regeneration. (A) The dorsal motor nerve (green), innervating the dorsal myotome, was laser-transected near the level of the spinal cord exit point, without affecting the integrity of ventral motor nerve (black), innervating the ventral myotome, in 5-day post fertilization zebrafish larvae. 0hpi: 0 hours post injury. (B) 7–15 hours post injury (hpi) the regenerating dorsal motor axons are actively probing the environment in search for their initial trajectories. Schwann cells proximal to the lesion site upregulate the expression of the glycosyltransferase lh3, a transmembrane protein located on the rough endoplasmatic reticulum (rER), resulting in increased secretion of collagen4α5 (col4α5). The repellent molecule slit1a was found to co-localize with the col4a5. Nu: nucleus. (C) 48 hours post injury the misdirected axons (gray) destabilize possibly due to the collagen4α5 dependent accumulation of slit1a, while the rest stabilize and grow toward their original trajectories.
