Figure 2.
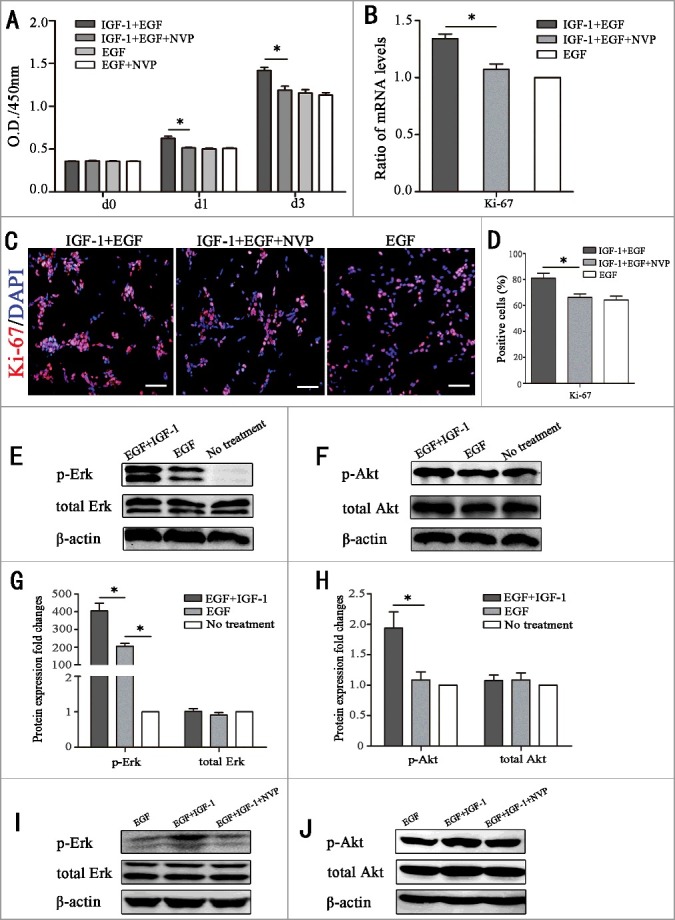
IGF-1 promotes the proliferation of RPCs through the membrane receptor IGF-1R by targeting the AKT and Erk signaling pathways. (A) The CCK-8 analysis of RPC proliferation in EGF+IGF-1 plus NVP-ADW-742 (chemical inhibitors of IGF-1, NVP), EGF+IGF-1, EGF and EGF+NVP. The O.D.450 values on day 1 and day 3 were remarkably decreased in the IGF-1+EGF plus NVP group compared to the IGF-1+EGF group. And the O.D.450 values on day 1 and day 3 had no statistical difference between EGF group and EGF group plus NVP. (B) Ki-67 qPCR expression of RPC proliferation in IGF-1+EGF cultures, IGF-1+EGF cultures with NVP, and EGF cultures. The results showed that the mRNA expression level of Ki67 in the IGF-1+EGF plus NVP cultures was lower than that of the IGF-1+EGF group, but there is no significant difference between IGF-1+EGF plus NVP group and EGF group. (C-D) The immunocytochemistry analysis of the percentages of Ki-67-positive cells in the RPC cultures treated with IGF-1+EGF plus NVP, IGF-1+EGF and EGF. The percentages of positive cells were decreased in the RPC cultures treated with IGF-1+EGF plus NVP compared to the IGF-1+EGF group, but there is no significant difference between IGF-1+EGF plus NVP group and EGF group. (E-H) The RPCs were not treated (no treatment group) or were treated with EGF or IGF-1 plus EGF for 20 min, and the protein extracts were assessed by Western blot analysis using antibodies against specific phosphorylated residues (p-Akt and p-Erk) or the total protein (Akt and Erk). The results showed that IGF-1 caused stronger phosphorylation of Akt and Erk. (I-J) The RPCs were stimulated with IGF-1 (20 ng/mL) in the presence of NVP, and the promotion phosphorylation of Akt and Erk caused by IGF-1 were attenuated by NVP. * P ≤ 0.05 (ANOVA test). Scale bar: 100 μm.
