Figure 3.
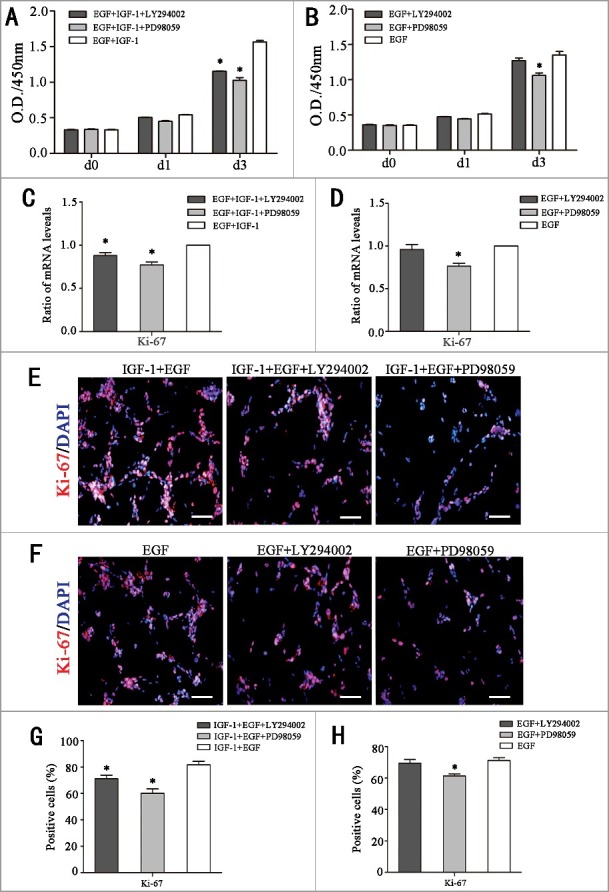
IGF-1 promotes RPC proliferation by targeting the PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk signaling pathways. (A-B) RPCs were stimulated with IGF-1 plus EGF or EGF in the presence of LY294002 (chemical inhibitor of Akt) or PD98059 (chemical inhibitor of Erk), and the RPCs’ growth was measured by CCK-8 analysis. Both LY294002 and PD98059 can weaken RPC proliferation, while only PD98059 can reduce EGF-1-induced RPC proliferation instead of LY294002. (C-D) Detection of the mRNA levels of Ki-67 in the RPCs that were treated with IGF-1 plus EGF or EGF in the presence of LY294002 or PD98059. The results showed that IGF-1+EGF-induced mRNA levels of Ki-67 can be reduced by both LY294002 and PD98059 while EGF-induced mRNA levels of Ki-67 only can be reduced by PD98059. (E-H) Ki-67 immunocytochemistry results are in accordance with the mRNA levels of Ki-67: an IGF-1+EGF-induced positive cell ratio of Ki-67 can be reduced by both LY294002 and PD98059, while an EGF-induced positive cell ratio of Ki-67 only can be reduced by PD98059. * P ≤ 0.05 (ANOVA test). Scale bar: 100 μm
