Figure 3.
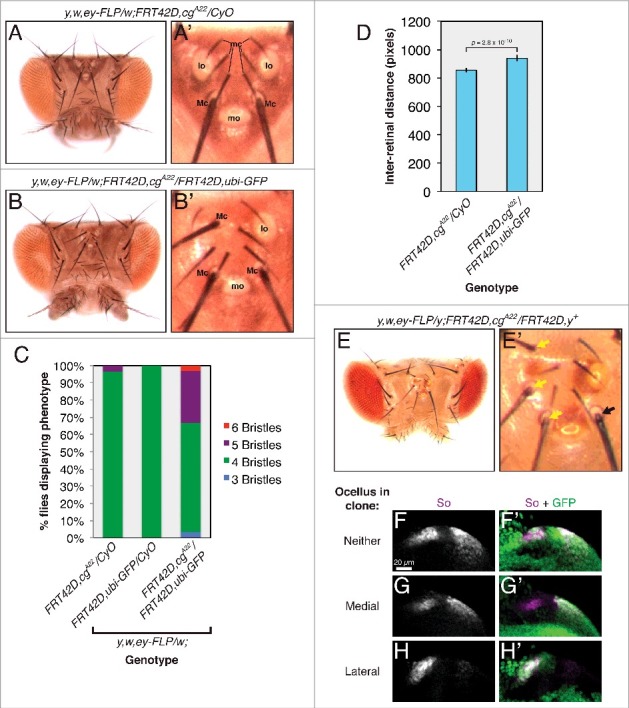
cg controls fate specification in the head vertex. Dorsal views of adult heads are oriented posterior up. For larval tissues, all images are zoomed views of the developing head vertex in late third instar eye imaginal discs, oriented anterior to the left and dorsal up. (A) The wild type arrangement of structures in the adult head vertex (zoomed view in A'). mc: microchaetae; lo: lateral ocellus; Mc: macrochaetae; mo: medial ocellus. (B) Lateral ocelli are lost and ectopic macrochaetae form in flies carrying cg clones. Note three macrochaetae, one protruding from between the microchaetae, in the zoomed view in B'. (C) The number of head vertex macrochaetae in control flies or those carrying cg clones. n > 28 for each genotype. (D) The inter-retinal distance increases in flies carrying cg clones. (E) Ectopic macrochaetae arise from cg null tissue marked by yellow (y). Zoomed view in E'. Yellow arrows mark y macrochaetae. The black arrow marks a wild type y+ bristle. (F) So expression marks the two ocellar fields in a wild type head vertex. Wild type cells are marked with GFP. (G) So expression is subtly reduced in the presumptive medial ocellus compared to the lateral field in cg null clones (marked by the absence of GFP). (H) So expression is lost in cg mutant lateral ocellar fields.
