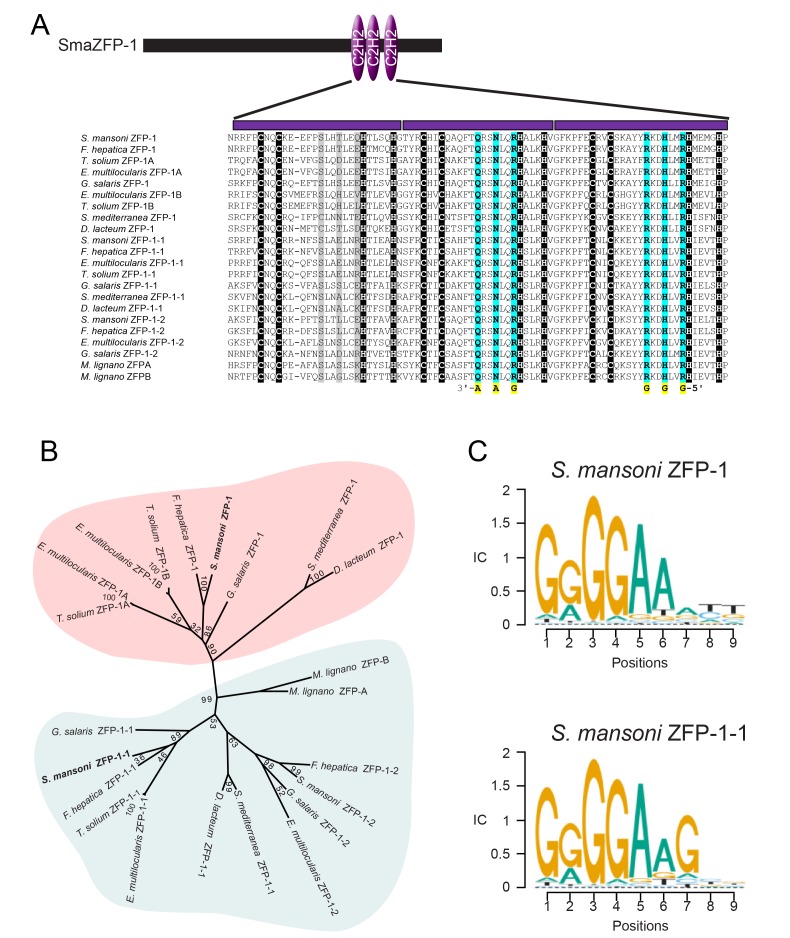
Figure 4. ZFP-1 and ZFP-1–1 are flatworm specific zinc finger proteins and are putative transcriptional regulators.
(A) Multiple protein sequence alignment of the C2H2 domain of several zfp-1 and zfp-1–1 homologs. Zinc coordinating residues are shown in black background. Conserved residues contributing to high specificity DNA-binding are highlighted in cyan for the second and third zinc fingers, with the specific DNA base shown below the residue highlighted in yellow. The corresponding positions in the first zinc finger are shown in grey background. The positions determining DNA binding specificity in the first zinc finger (highlighted in grey background) either are not well conserved among these proteins or do not contribute to high specificity of DNA binding. (B) Un-rooted phylogenic tree of ZFP-1 and ZFP-1–1 homologs from multiple species of flatworms. Numbers at the nodes represent bootstrap values. (C) Predicted DNA binding motif of zfp-1 and zfp-1–1 of S. mansoni by the ZFModels server.