Extended Data Figure 9. rDNA damage impairs DDX21 functions and causes craniofacial deformities.
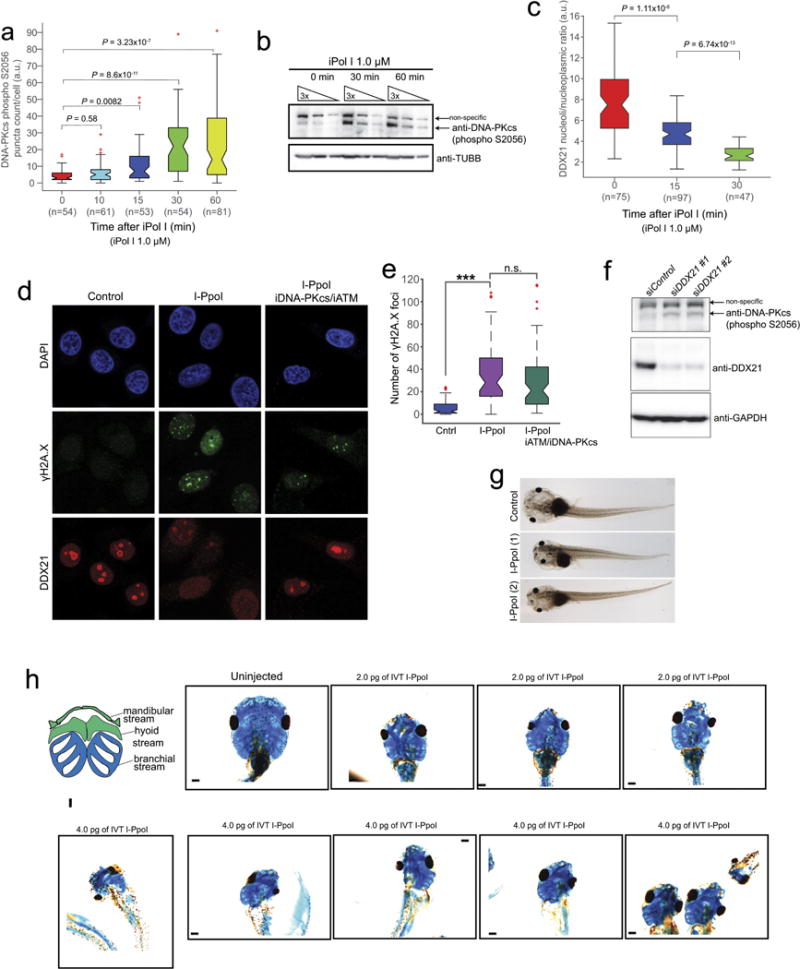
a, b, Time course of phosphorylated DNA-PKcs as measured by auto-phosphorylation of the kinase in Ser2056 (S2056) upon iPol I treatment. Cells were collected from n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Boxes represent median value and 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers are minimum to maximum, crosses are outliers. P, two-sided Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test. c, Time course of DDX21 exclusion from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm upon iPol I treatment. Cells were collected from n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Boxes represent median value and 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers are minimum to maximum, crosses are outliers. P, two-sided Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test. d, Representative immunofluorescence images of HeLa cells transfected with in vitro transcribed I-PpoI and treated or not with inhibitors for ATM (iATM) and DNAPK (iDPK). After treatment, cells were stained with antibodies against DDX21 and γH2A.X. e, Box plot quantifying the number of γH2A.X foci of HeLa cells transfected with I-PpoI and treated or not with iATM and iDPK. Cells were collected from n = 3 biologically independent experiments. Boxes represent median value and 25th and 75th percentiles, whiskers are minimum to maximum, crosses are outliers. ***P < 0.001, two-sided Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test, not significant (NS). f, Western blot showing DNA-PKcs by auto-phosphorylation of S2056 upon knockdown of DDX21. Two different siRNAs were used in this experiment (see Methods for details). n = 3 biologically independent experiments. g, Representative bright-field images of stage 49 Xenopus embryos either uninjected or injected with in vitro transcribed I-PpoI and (h) alcian blue stainings of Xenopus cranial cartilage from embryos injected with the indicated doses of in vitro transcribed I-PpoI. Embryos were collected from n = 4 biologically independent injections.
