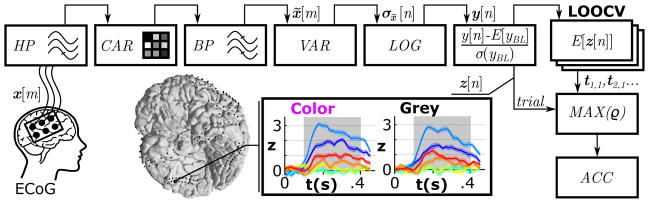
Figure 4.
Feature extraction pipeline and classification method for the assessment (experiment I). Signal processing steps for the multi-channel ECoG signals x[m] included drift removal by a high-pass filter (HP), spatial filtering (CAR), temporal band-pass filtering (BP), variance estimation (VAR), log-transformation (LOG) and standardization (z-score). Colored time series show the mean z-scores (z[n]) with standard errors for all stimulus types (color codes are based on Figure 1) from ECoG electrode location 182 of subject A. Areas shaded in grey represent the active period used for discrimination. One active period (trial) of z[n] was correlated with templates (t1,1,tt2,1…) based on the remaining trials of each stimulus type. The template that correlated most strongly (MAX(ρ) assigned the trial class according to the template class. A leave-one-out cross validation (LOOCV) yielded the classification accuracy (ACC) of all trials and stimulus types.