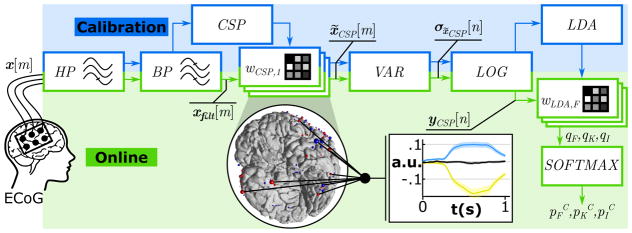
Figure 5.
Feature extraction pipeline and classification method for real-time detection and discrimination in experiment II and III. Calibration: Recorded multi-channel ECoG signals x[m] were HP and BP filtered and submitted to a common spatial pattern (CSP) analysis that computed a set of spatial filters (wCSP). Spatially filtered signals x̃CSP [m] underwent variance estimation (VAR) and log-transformation (LOG) and resulted in normalized yCSP [n]. A linear discriminant analysis (LDA) generated class specific weights (wLDA) for real-time processing. Online: Real-time processing steps included the HP and BP filtering and the spatial (wCSP) filtering, followed by the variance estimation (VAR) and log-transformation (LOG). The linear classifier (wLDA) weighted the features in yCSP [n] and generated LDA outputs (qF,qK,qI) for Face, Kanji and Idle. Finally, a Softmax function transformed the LDA output in complementary probabilities (pFC,pKC,pIC). The diagram yCSP [n] shows the real-time processing output for Face (blue), Kanji (yellow) and Idle (black) based on 182 combined ECoG locations in subject A.