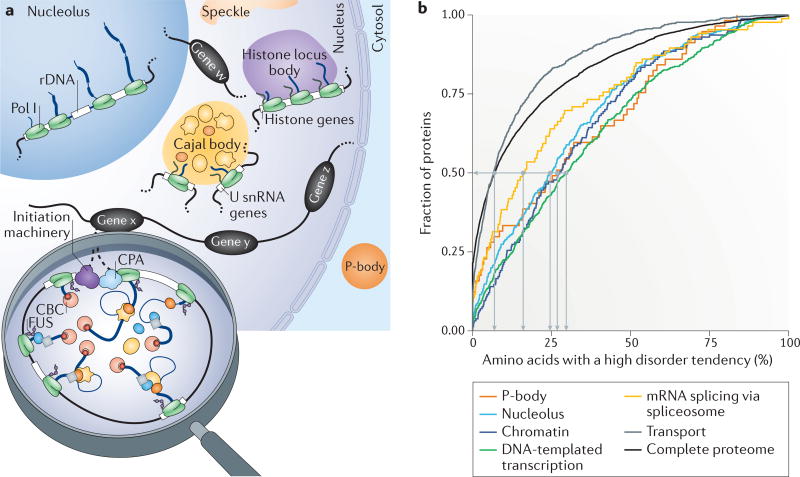
Figure 6. Higher-order organization of the gene expression machineries.
a | The nucleus and cytoplasm contain membrane-less compartments, known as bodies, such as the nucleolus, Cajal bodies, histon locus bodies, speckles and P-bodies. Such bodies form through liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS) and are often linked to the transcription of specific genes, for example, ribosomal DNA (rDNA) in the nucleolus, small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes in Cajal bodies and histone genes in histone locus bodies. We propose that looped and actively transcribed genes (genes w, x, y and z) are also likely to form nuclear bodies. b | Spliceosome proteins, particularly chromatin and transcription-associated proteins, are predicted to have a similar proportion of unstructured protein regions to those of other groups of proteins that are known to be involved in LLPS, as shown in the cumulative representation of the complete proteome and the protein groups associated with specific Gene Ontology terms (cellular component: P-body, nucleolus, chromatin (binding); biological process: DNA-templated transcription, mRNA splicing via spliceosome and transport). The data were downloaded from the Saccharomyces Genome Database (Supplementary information S3 (table)). The cumulative fraction of proteins (y axis) is given in association with the percentage of amino acids per protein that have a high probability of being in a disordered region (x axis), according to predictions by IUPred184,185. Whereas 50% of transport proteins and the entire proteome contain 7% or fewer amino acids with a high tendency to form disordered regions, 50% of the P-body, nucleolar or chromatin and transcription-associated proteins contain 25–30% of such amino acids. The median fraction of amino acid disorder tendency for spliceosomal proteins is 16%. Medians are represented by light grey lines. CBC, cap-binding complex; CPA, cleavage and polyadenylation complex; Pol I, RNA polymerase I.