Figure 7.
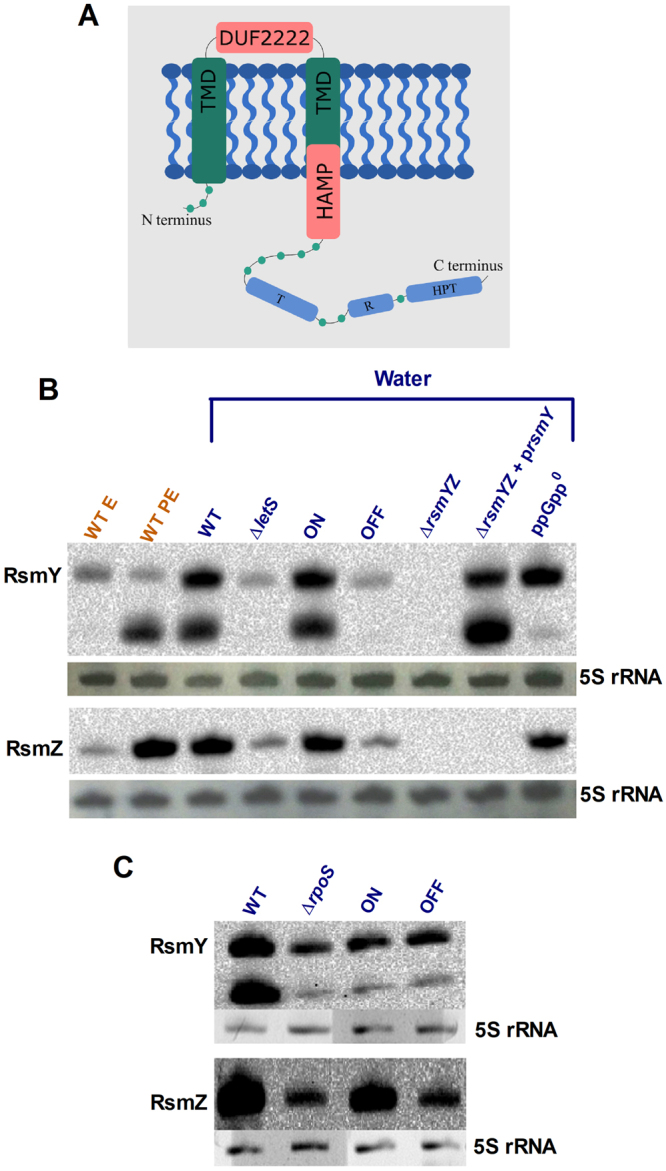
LetS topology and the impact of the stringent response elements, RpoS and ppGpp, on RsmY/Z expression. (A) Topology of the LetS protein was determined using the NCBI CDD Web server, as well as TMHMM v.2.0 and TOPCON software. Transmembrane domains (TMD) are represented by green boxes. Two putative signal sensing domains (pink boxes) are also predicted; a DUF2222 domain is located between the two TMD, and a HAMP domain overlaps the C-terminus of the second TMD. The transmitter (T), receiver (R) and phosphotransfer (HPT) domains that are involved in signal transduction are represented by light blue boxes. (B) The sRNAs RsmY (top) and RsmZ (bottom) under LetS control were probed to determine their levels in water and the influence of ppGpp on their expression. The first two lanes represent the WT strain grown in rich broth to the exponential (E) or the post-exponential (PE) phase. The remaining wells represent the respective strains exposed to water for 2 hours. (C) Impact of RpoS on the expression of RsmY/Z. The sRNAs RsmY (top) and RsmZ (bottom) under LetS control were probed to determine their levels in water. The WT (JR32), rpoS mutant, the induced (ON) or uninduced (OFF) ∆rpoS + prpoS strains were exposed to water for 2 hours. 1 μg of RNA was loaded into each well. Acrylamide gels were stained with ethidium bromide to visualize the 5 S rRNA loading control (shown beneath the respective blots). See Supplementary Figs S5 and S6 for complete gel and blot images.
