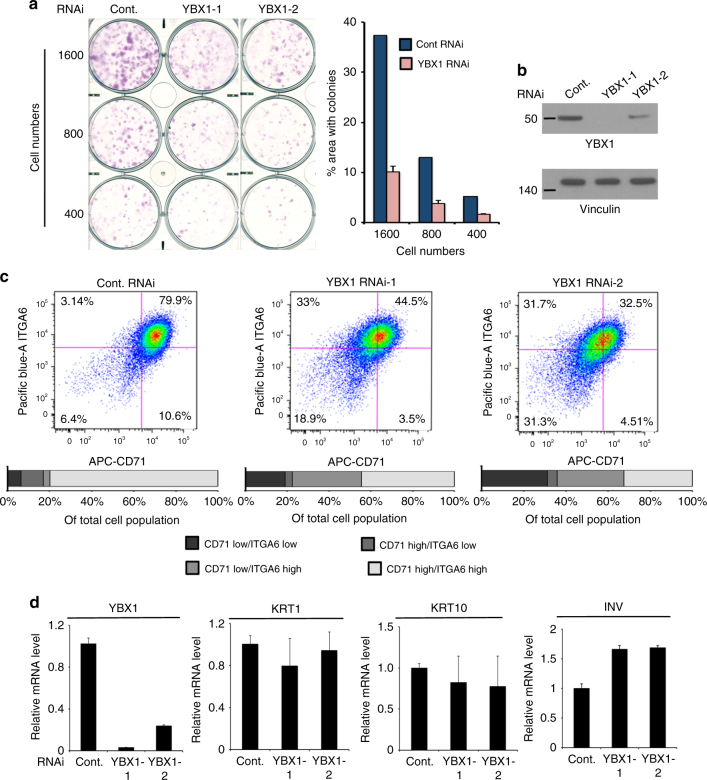
Fig. 4.
YBX1 depletion in primary human keratinocytes results in epidermal progenitor defects without affecting commitment to differentiation. a Colony formation capacity of primary human keratinocytes transfected either with a control siRNA or two different YBX1 siRNAs was assessed by a clonogenic assay; 400, 800, or 1600 cells per well were seeded in 6-well plates and incubated for 10 days. Cells were fixed and stained using Sulforhodamine B (SRB). % area with colonies was calculated using ImageJ. Average and SDs were calculated based on the two different siRNAs results. b YBX1 protein levels in keratinocytes transfected with control or YBX1 siRNAs (from a) were assessed using western blotting, and vinculin levels served as a loading control. c YBX1 depletion reduces the population of actively cycling epidermal progenitors: passage 2 of primary human keratinocytes pooled from three different donor cultures were transfected with either control siRNA or two different YBX1 siRNAs and sorted for expression of CD71 and Integrin-α6 (ITGA6) by a flow cytometer after staining with APC-conjugated anti-CD71, and Pacific blue-conjugated anti-ITGA6 antibodies. Quantification of the separate populations of cells is presented in the lower panel as % of the whole population. d Control and YBX1 siRNA transfected human keratinocytes were harvested 4 days after transfection and mRNA levels of the differentiation markers KRT1, KRT10, and INV were quantified by qRT-PCR using 36B4 mRNA as an internal control. Error bars represent mean SD, n = 3