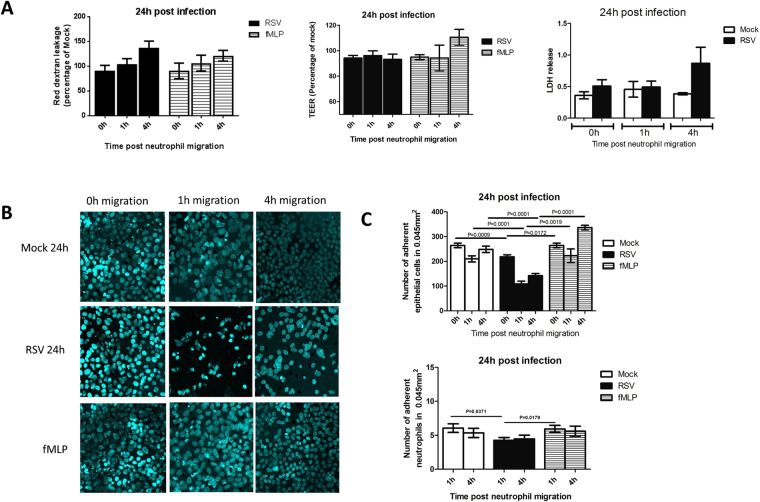
Figure 6.
Damage caused by neutrophil migration through epithelial monolayers infected with RSV for 24 hours. (A) The damage caused to the A549 epithelium following neutrophil migration through cells infected with mock or RSV infection for 24 hours as determined by (i) Red-dextran leakage from basal-apical compartments, data represented as the percentage relative to the mock infected control n = 4 (ii) TEER as measured using a voltohmmeter, data is represented as the percentage relative to the mock infected control n = 9 (iii) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release as measured in apical supernatant of AECs post neutrophil migration. The neutrophil chemoattractant N-Formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) was used as a positive control Bars show mean ± SEM of at least n = 3 biological repeats. (B) Representative microscopy images of A549 epithelial monolayers infected with RSV for 24 hours stained with a nuclei stain (Hoechst) following neutrophil migration after 1 or 4 hours. (C) Epithelial cell and neutrophil nuclei were counted in ImageJ and the average number of nuclei from all images was calculated. Bars show mean ± SEM of n = 5 biological repeats. Statistical significance is shown. For all other comparisons P > 0.05.