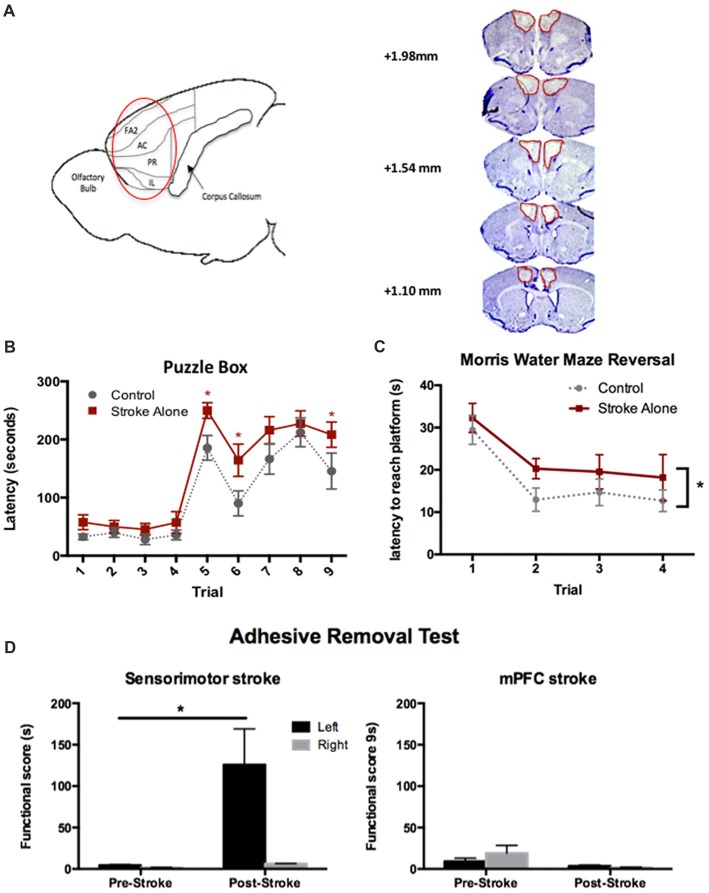
Figure 1.
Endothelin-1 (ET-1)-induced cognitive model of stroke in mice. (A) Sagittal representation of the lesioned areas of the brain (circled). FA2, frontal area 2; AC, anterior cingulate cortex; PR, prelimbic; IL, infralimbic; cresyl violet stained coronal sections depicting typical medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) lesion on day 4 post-stroke. (B) Significant cognitive impairments following stroke were detected using the Puzzle Box (PB) task at day 4–6 compared to control (n = 18 stroke; 16 control). (C) Following stroke, a significant cognitive deficit was detected up to 45 days, using the Morris Water Maze (MWM) reversal test (n = 12 stroke; 10 control). (D) Post-stroke functional scores in the adhesive removal test. Unilateral sensory-motor (n = 3), but not bilateral mPFC (n = 7) stroke, resulted in contralesional (left) forepaw deficits compared to baseline performance. *p < 0.05.