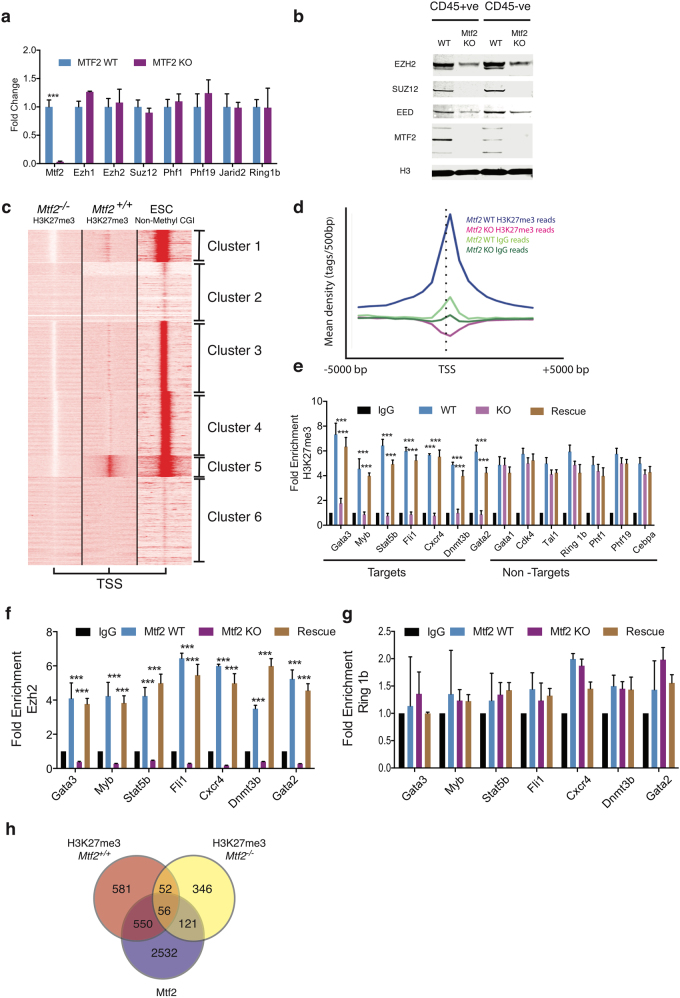
Fig. 3. Mtf2 is required for promoter-proximal histone trimethylation of lysine 27 within fetal liver erythroid progenitors.
a Transcript levels of PRC2 complex members, Suz12, Ezh1/2 and Jarid2, as well as PRC1 component Ring1b are unchanged in Mtf2−/− CD45+ FL cells as determined by RT-qPCR. b Core PRC2 proteins Ezh2, Suz12 and Eed are downregulated along with Mtf2 in both CD45+ and CD45- FL cells from Mtf2−/− mice. H3 was used as a protein loading control, and representative images are shown. c The k-mean clustering identifies patterns of H3K27me3 enrichment in primary CD71+ Ter119+ erythroblasts. Globally, a loss of enrichment centered around transcriptional start sites (TSS) is observed in CD71+ Ter119+ cells lacking Mtf2, which correlates with non-methylated CpG islands in ESCs within the same genomic regions. d H3K27me3 ChIP-seq density of reads is plotted within 5 kb of the TSS within one cluster of approximately 2400 genes (Cluster 5). In these genes, H3K27me3 binding is specifically reduced immediately around the TSS in Mtf2-null CD71+ Ter119+ cells. e WT and Rescue conditions are compared to KO. Validation of targets and non-targets from H3K27me3 ChIP-seq results performed by ChIP-qPCR. Rescuing Mtf2 expression by overexpressing Mtf2 within Mtf2-deficient CD71+ Ter119+ cells resulted in increased H3K27me3 binding at positive target loci. f, g ChIP-qPCR analysis revealed f a loss of Ezh2 binding and g no changes in Ring 1B binding within TSS regions that showed loss of H3K27me3 marks, when WT and Rescue conditions are compared to KO. h Overlap of genes associated with binding sites identified by ChIP-seq. In all, 1131 genes have lost H3K27me3 marks upon loss of Mtf2/PRC2 and 550 of those targets also show Mtf2 binding. See also Supplementary Figures S3-S4. ***P < 0.001