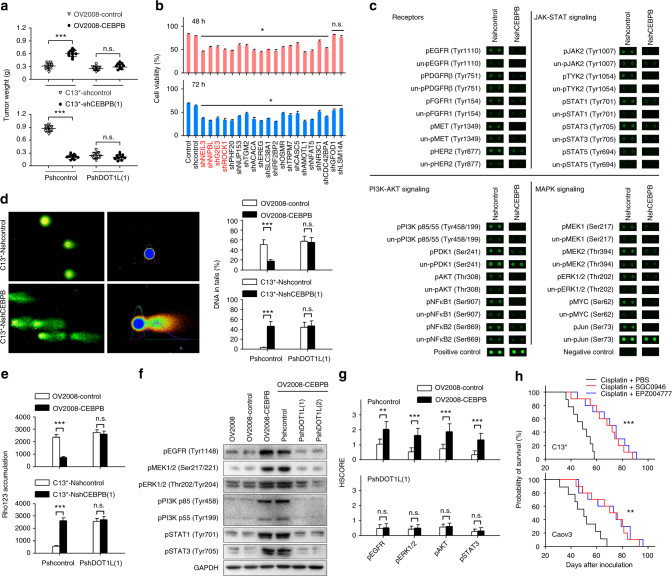
Fig. 6.
The effects of C/EBPβ on cisplatin resistance are mediated by DOT1L. a One week after orthotopic inoculation with the indicated cells, the mice were treated with cisplatin (5 mg/kg) intraperitoneally every 4 days; for DOT1L inhibitor treatment, 4 mg/kg SGC0946 or EPZ004777 were injected intraperitoneally every 4 days (n = 10 per group). Tumors were excised and weighed 6 weeks after tumor inoculation. b Assay of cisplatin-resistance genes. Genes were individually silenced by shRNA lentiviral particles in SKOV3 cells, and cell viability at 48 h and 72 h after treatment with 30 μM cisplatin was determined using CCK8 assays. c Phospho-antibody array. See Supplementary Figure 21 and Supplementary Data 7 for full results and additional annotations. d Alkaline comet assays were performed after treatment with 50 μM cisplatin for 24 h. e Cellular accumulation of rhodamine 123 (Rho123) was determined by flow cytometric analysis after treatment with 1 μM Rho123 for 1 h. f The indicated cells were treated with 50 μM cisplatin for 24 h, and protein phosphorylation was detected by western blotting. g IHC analysis of phosphorylated EGFR, ERK1/2, AKT, and STAT3 in xenograft tumor sections collected from mice treated with cisplatin (n = 10 per group). h The mice were treated as described above in a. The mice were maintained until death, and Kaplan–Meier survival curves of mice were plotted. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Figure 26. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. n.s. not significant