Figure 7.
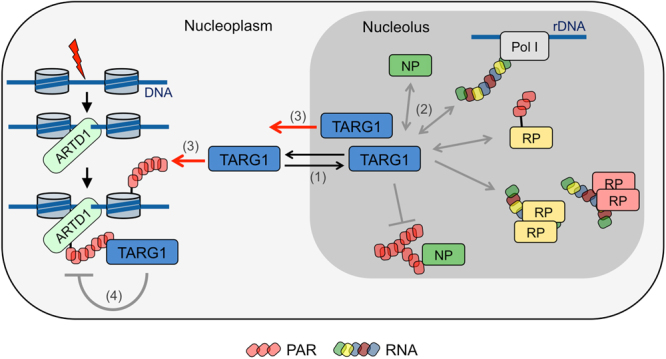
Model of a dual function of TARG1 in both RNA- and PAR-regulated cellular processes. Under steady-state conditions, TARG1 accumulates in nucleoli but constantly shuttles between nucleoli and the nucleoplasm (1). Accumulation of TARG1 in nucleoli is mediated by direct interaction with ribosomal RNA or proteins (RP) or other nucleolar proteins (NP; 2). PARylation modulates the localization and interactome of TARG1. TARG1 re-locates to the nucleoplasm upon DNA damage-induced ARTD1/2-dependent PARylation (3). In nucleoli, TARG1 may contribute to ribosome biogenesis, e.g., by counteracting PARylation of RPs or controlling nucleolar PAR scaffolds. DNA damage-induced PARylation might serve to sequester TARG1 to the nucleoplasm to regulate PAR turnover at DNA damage sites (4). Hypothetical interactions are marked by grey arrows.
