FIGURE 1.
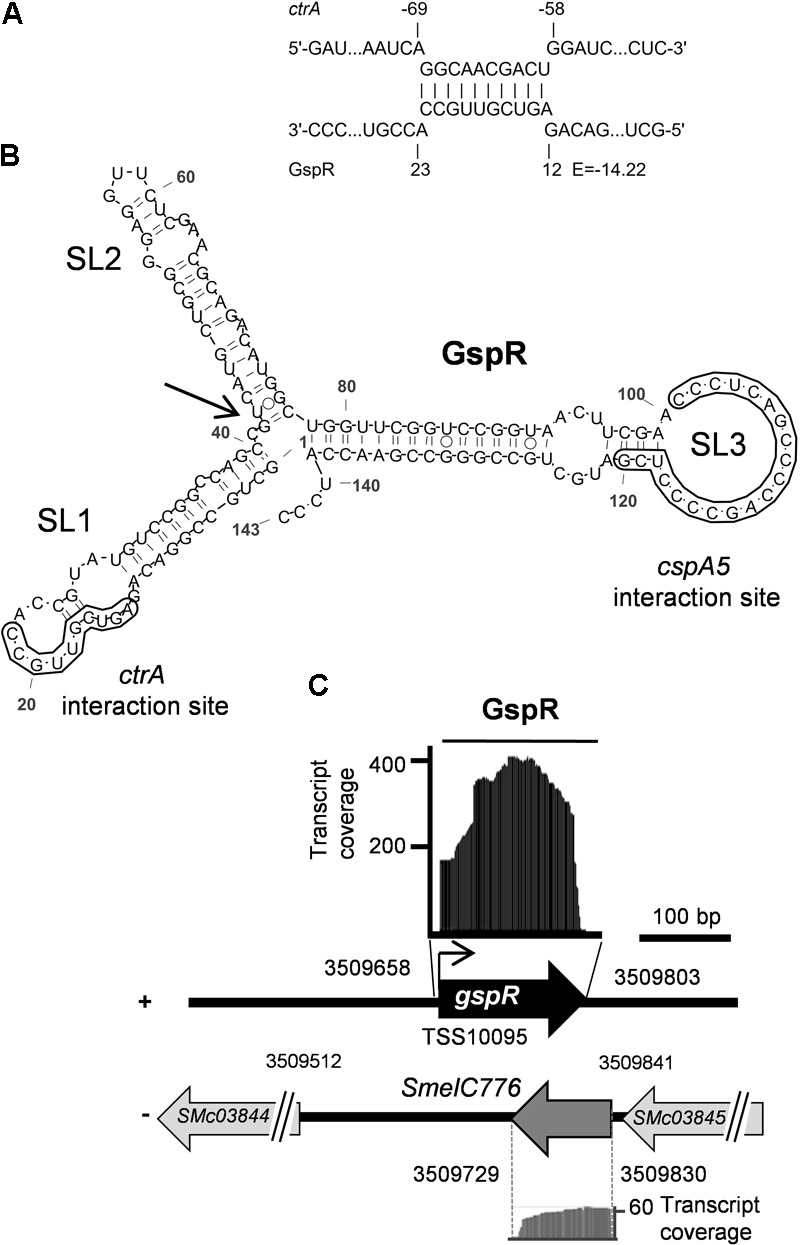
ctrA 5′ UTR is predicted to bind to GspR (SmelC775). (A) Predicted thermodynamically favored antisense interactions between GspR and ctrA mRNA. Numbers denote nucleotide positions relative to the TSS of gspR and the start codon of the putative target mRNAs. The predicted energy score (E) is indicated in kcal/mol. (B) Predicted secondary structure of the full-length GspR transcript with a minimum free energy of -66.30 kcal/mol exhibiting three independent stem loop (SL1 to SL3) structures. Nucleotide positions relative to the 5′-end are indicated. The SL1 and SL3 regions predicted to interact with the ctrA and the cspA5 mRNAs, respectively, are boxed. (C) gspR genomic locus. Genes predicted on the complementary strand (-), including the SmelC776 locus are shown. Genome coordinates are indicated. RNAseq coverage profiles of both GspR and SmelC776 in S. meliloti Rm1021 are depicted. Black and gray areas represent coverage of GspR (SmelC775) and SmelC776, respectively, from samples enriched in processed transcripts (Schlüter et al., 2010). The angled arrow marks the GspR 5′-end (TSS10095) and the horizontal bar indicates the full-length 144 nt GspR sequence used for structure prediction.
