Figure 1.
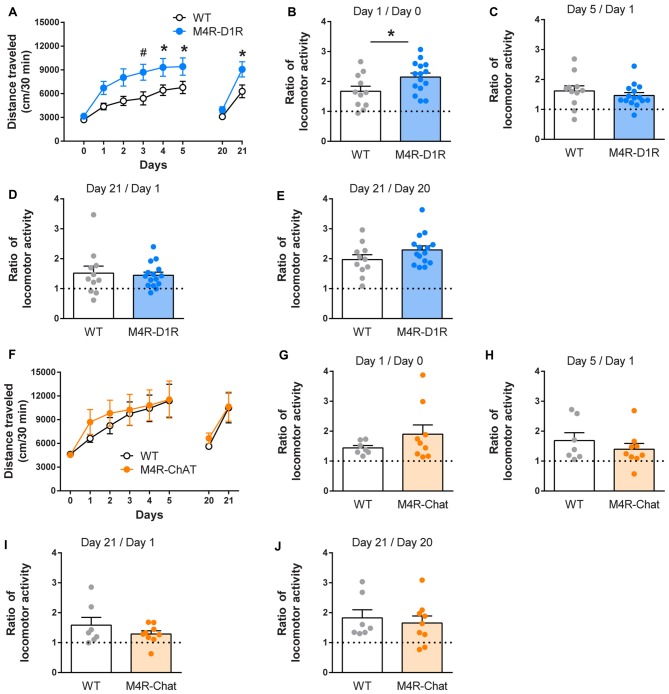
Cocaine-induced locomotor responses are elevated in muscarinic M4 receptor (M4R)-D1RCre mice. M4R-D1RCre mice increased their locomotor response to repeated 15 mg/kg cocaine injections (i.p.) to a greater degree than wildtype littermate controls (A) (n = 11 WT, n = 15 M4R-D1R). Acute cocaine-induced locomotion was increased in M4R-D1RCre mice compared to controls (B). Locomotor sensitization (the ratio between day 1 and 5 or between day 1 and 21) remained unchanged (C,D), this was also the case for cocaine-induced locomotion after the sensitization protocol (E). In contrast, the locomotor response of M4R-ChATCre mice did not differ from WT mice at any time point (F–J) (n = 7 WT, n = 9 M4R-ChAT). *p < 0.05 repeated measure one-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test (A) or Student’s unpaired t-test (B), #p < 0.05 two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test for genotype difference (A).