Figure 2.
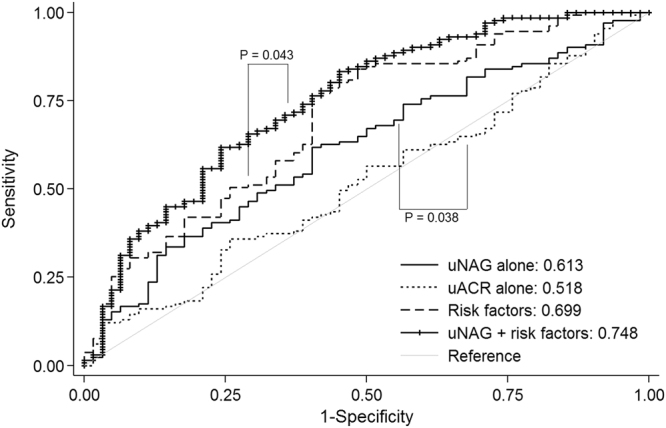
Measurement of uNAG improved the identification of subjects with higher G/A ratios, in addition to conventional risk factors such as uACR. The solid line, very short dash line, dash line, and line with small cross represent the discriminatory ability characterized by the area under the curve (AUC) for log-uNAG alone, log-uACR alone, for the model that included conventional risk factors (log-uACR, age, sex, BMI, diabetes duration, angiotensin blocker use, eGFR, and fasting plasma glucose level), and for the composite of log-uNAG and the conventional risk model, respectively. Abbreviations: log-uNAG, log-transformed urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase; log-uACR, log-transformed urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio; ROC, receiver operating characteristics curve; BMI, body mass index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; G/A ratio, glycoalbumin-to-hemoglobin A1c ratio.
