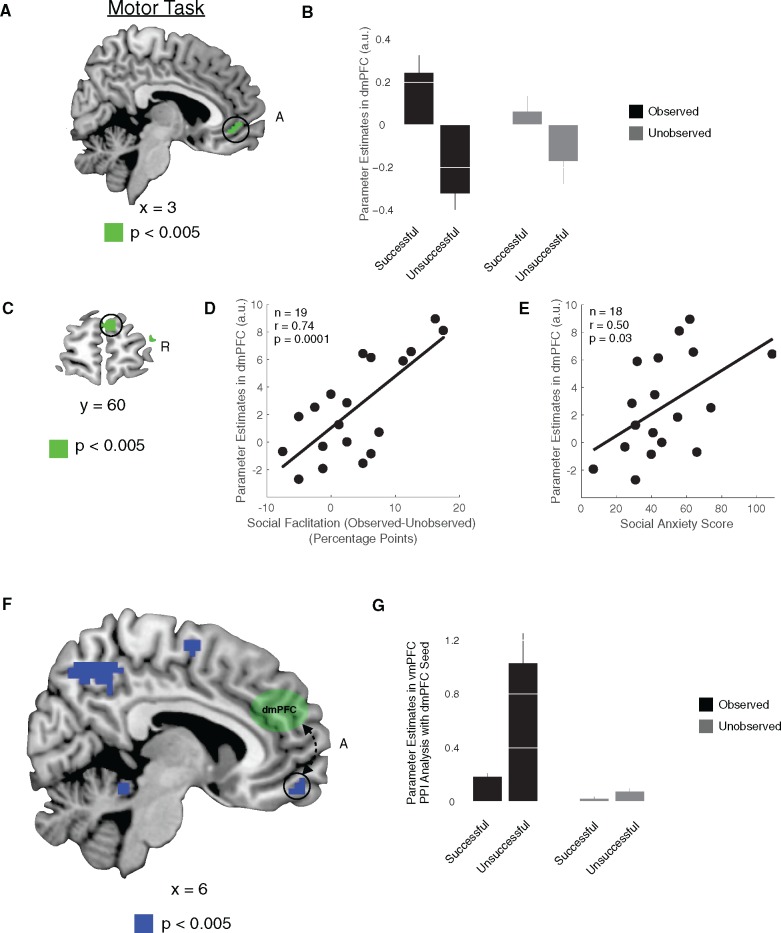
Fig. 2.
Neural representations of value and social facilitation. (A) At the time of task execution, vmPFC exhibited significant increases in signal when comparing conditions in which participants’ performance was successful and unsuccessful. (B) A significant interaction in vmPFC was found between observation conditions and performance. (C) Activity in dmPFC was positively modulated by an individual’s propensity for social facilitation. Between-participant regression analysis considering the difference in performance between the observed and unobserved conditions as a covariate for observation-related activity in dmPFC (i.e. difference between the observed and unobserved imaging conditions) (D) Plot of the correlation between activity in the dmPFC and social facilitation of performance (i.e. illustration of Figure 2C). (E) Plot of the correlation between activity in the dmPFC and social anxiety scores. (F) A connectivity analysis with dmPFC seed found that the functional coupling between dmPFC and vmPFC was significantly increased during trials in which participants were observed and they were unsuccessful. (G) Bar plot of the vmPFC PPI effects for the observed/unobserved conditions and successful/unsuccessful performance. All contrasts are significant at P < 0.05, small volume corrected. Error bars denote SEM. R, right. A, anterior.