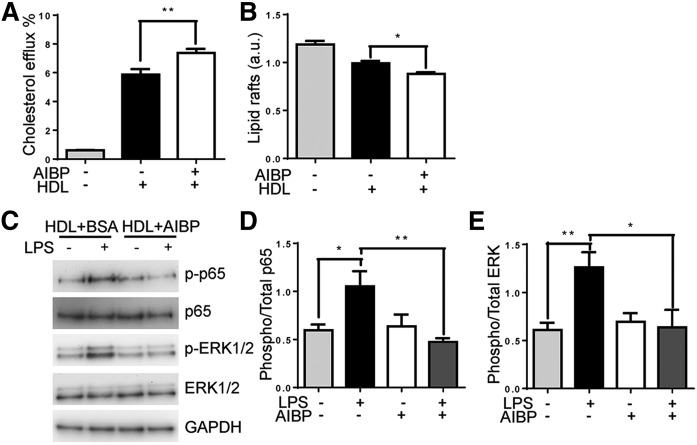
Fig. 7.
AIBP facilitates cholesterol efflux and reduction in lipid rafts and inhibits macrophage inflammatory signaling. A: Cholesterol efflux from macrophages. RAW264.7 macrophages were loaded for 24 h with 2 µCi/ml [3H]cholesterol, and then efflux was stimulated by 25 µg/ml HDL treatment in the presence or absence of 0.2 µg/ml AIBP for 4 h (n = 14 for HDL-containing samples; n = 2 for media only). B: CTB binding was quantified via FACS to determine lipid raft content. RAW264.7 macrophages were loaded with acetylated LDL and treated for 4 h with media only or 25 µg/ml HDL in the presence or absence of 0.2 µg/ml AIBP or BSA (n = 3). a.u., arbitrary units. C: RAW264.7 macrophages were stimulated with 10 ng/ml LPS for 30 min, in the presence of BSA or AIBP. Phosphorylation of p65 and ERK1/2 were assessed via gel electrophoresis and Western blotting of cell lysates. D: Quantification of p65 phosphorylation (n = 5). E: Quantification of ERK phosphorylation (n = 6). Mean ± SEM; *** P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01; * P < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA).