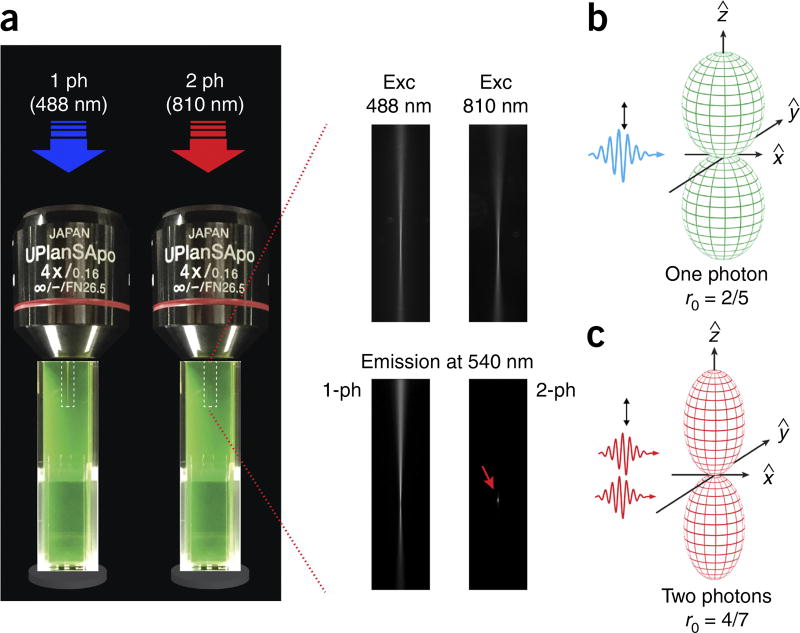
Figure 2.
One-photon versus two-photon excitation. (a) Comparison between one- and two-photon excitation and emission beam profiles in a fluorescein solution. For two-photon excitation, the emission is confined within a smaller focal point (red arrow in lower right-hand image), allowing for accurate optical sectioning imaging and accurate probing of volumes on the order of or below a femtoliter. A dry 4× objective was used for the demonstration of one- and two-photon fluorescence in order to distance the two-photon spot from the edge of the cuvette. (b,c) Photoselection function for one-photon (b) and two-photon (c) excitation. The fundamental anisotropy (r) for one-photon excitation is equal to 2/5. Two-photon excitation yields a strongly aligned population with a photoselection function proportional to cos4 θ. The fundamental anisotropy in this case is higher and is equal to 4/7. Exc, excitation; ph, photon.