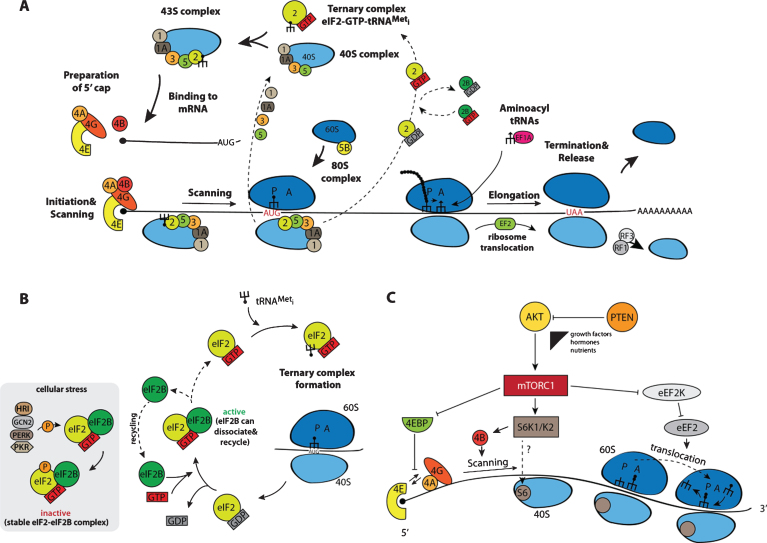
Fig.2.
Schematic representation of the process of protein biosynthesis in eukaryotes with main regulatory nodes. (A) Basic steps of translation beginning from the formation of the ternary complex transiting to the 43S complex, which, after loading onto an mRNA, scans the non-translatable region till the recognition of the initiation AUG resulting in the 48S complex assembly. After 60S subunit joining, newly formed 80S ribosomes proceed to elongation moving along the coding sequence until the stop codon appears in the acceptor A site of the ribosomes. This starts up the process of termination and recycling, releasing 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits for a new round of translation on the same or another mRNA molecule. (B) Regulation of the initiation of translation via the phosphorylation of factor eIF2 by stress-activated kinases HRI, PKR, GCN2, and PERK: phosphorylated eIF2 forms a very stable complex with the guanine exchange factor eIF2B exhausting the available pool of free eIF2B, thereby blocking the reaction of GDP-GTP exchange on eIF2. (C) mTORC1-mediated control including phosphorylation of 4E-BPs, S6K1/K2 and eEF2K. For more details, see the main text.