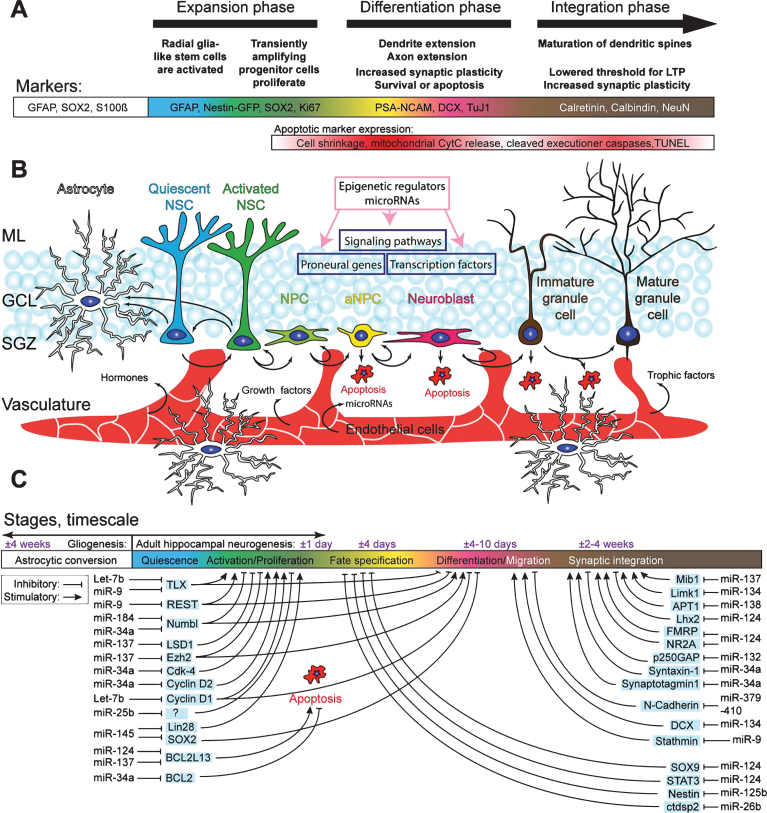
Fig.1.
Schematic overview of the hippocampal neurogenic niche, the different processes underlying AHN, and its regulation by microRNAs. A) Overview of the different stages of AHN. Each cell type can be identified by a combination of presence and absence of markers, combined with morphological cellular features. B) Overview of the neurogenic niche and the transition of a NSC into a mature neuron. The complexity of the neurogenic niche, consisting of multiple cell types in close association with the vasculature, allows for both local and distant cell communication. Distant cell communication occurs via factors released in the bloodstream, such as cell-extrinsic miRNAs, growth factors (VEGF and bFGF), hormones, and trophic factors (BDNF). Other cell-intrinsic factors, such as miRNAsm TLX signaling, notch signaling, and REST (purple boxes), and cell extrinsic factors such as HDACs, DNA methylation, and miRNAs (pink box), complete the coordinated regulated of AHN. C) MiRNAs regulate various key pathways important in AHN. Depicted are miRNAs of which a clear link with neurogenesis has been identified, together with their targets through which the miRNAs might exert their effect.