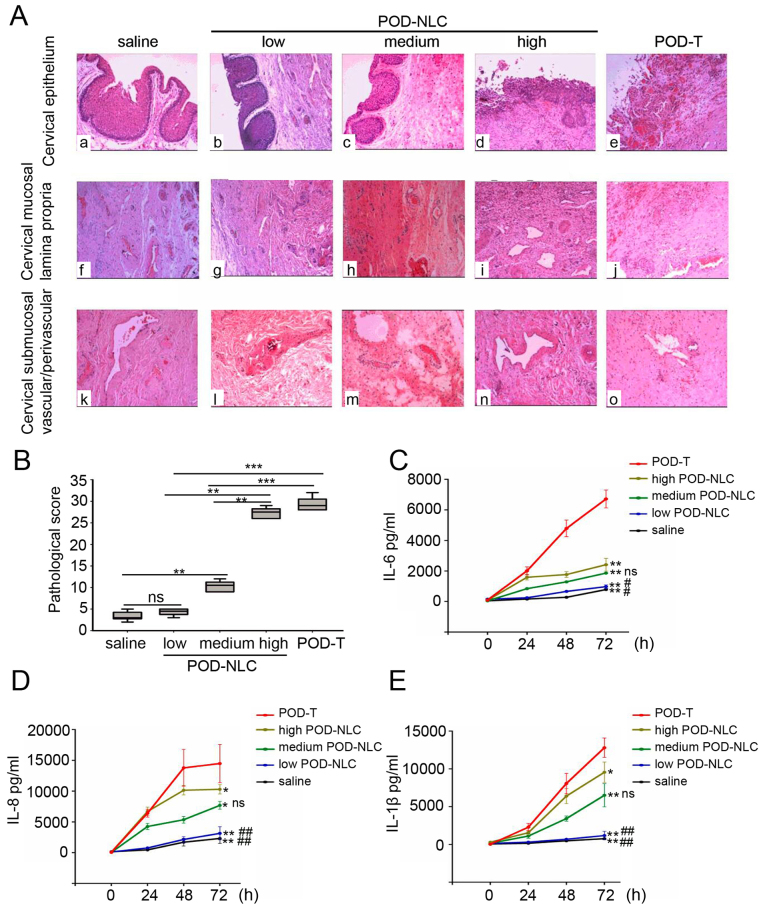
Figure 3.
POD-NLC causes decreased injury and expression of inflammatory cytokines in cervical mucous. (A) Histological alterations of the cervical mucosa following treatment with 0.5 ml normal saline (a, f and k), 0.5 ml 0.5% POD-NLC (b, g and l), 1.0 ml 0.5% POD-NLC (c, h, and m), 2.0 ml 0.5% POD-NLC (d, i and n) and 0.5 ml 0.5% POD-T (e, j, and o) were detected by hematoxylin and eosin staining (magnification, ×40). (B) Histopathological score of cervical mucosa treated with 0.5 ml normal saline, 0.5 ml 0.5% POD-T and 0.5% POD-NLC at different doses (0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 ml). ns, no significant difference; **P<0.01 and ***P<0.0001. Concentrations of inflammatory cytokines in cervical secretions were detected by Luminex instrument at 24, 48 and 72 h following treatment. The concentrations of (C) IL-6, (D) IL-8 and (E) IL-1β were detected in cervical secretions of pigs treated with 0.5 ml normal saline, 0.5 ml 0.5% POD-NLC, 1.0 ml 0.5% POD-NLC, 2.0 ml 0.5% POD-NLC and 0.5 ml 0.5% POD-T, respectively. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. the POD-T group. ns, no significant difference; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 vs. high-dose POD-NLC group. POD-NLC, podophyllotoxin-loaded nanostructured nanolipid carriers; IL, interleukin.